Pediatric Definition - Coarctation of Aorta
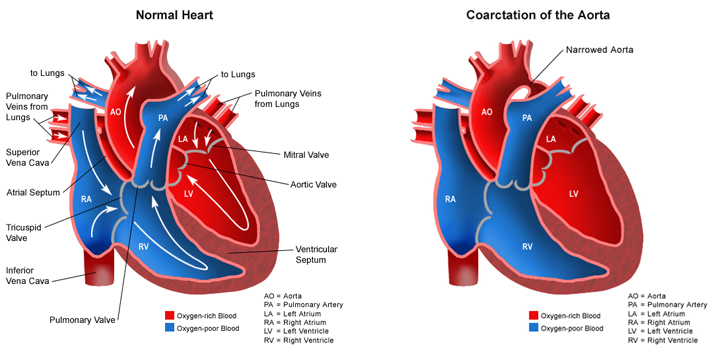
Coarctation of the Aorta
The symptoms and signs of coarctation of aorta may include diminished or absent of the femoral pulses with more than 20 mmHg differences between upper and lower extremity blood pressure.
On examination, patient may present with blowing systolic murmur on the back or left axilla.
The chest x ray may reveal left ventricular enlargement, indentation in the outline of the aorta at the coarctation, notching of the ribs due to enlargement of the intercostal collaterals and the present of aorta proximal to the coarctation.
The ECG may reveal left ventricular hypertrophy ( older children ) and right ventricular hypertrophy in infant.
ECHO may reveal the coarctation of the aorta.
The complication of the coarctation of the aorta may include systemic hypertension.
Coarctation of aorta can be treated with surgical correction and balloon angioplasty. Cath lab with transcatheter stent placement also is considered in treating coarctation of the aorta.
The symptoms and signs of coarctation of aorta may include diminished or absent of the femoral pulses with more than 20 mmHg differences between upper and lower extremity blood pressure.
On examination, patient may present with blowing systolic murmur on the back or left axilla.
The chest x ray may reveal left ventricular enlargement, indentation in the outline of the aorta at the coarctation, notching of the ribs due to enlargement of the intercostal collaterals and the present of aorta proximal to the coarctation.
The ECG may reveal left ventricular hypertrophy ( older children ) and right ventricular hypertrophy in infant.
ECHO may reveal the coarctation of the aorta.
The complication of the coarctation of the aorta may include systemic hypertension.
Coarctation of aorta can be treated with surgical correction and balloon angioplasty. Cath lab with transcatheter stent placement also is considered in treating coarctation of the aorta.