Medicine Notes - Clinical Procedures - Insertion Of Nasogastric Tube
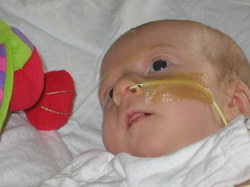
Insertion of the nasogastric tube
The indication for the insertion of the nasogastric tube include bowel obstruction, in poisoning cases to lavage the gastric content, stomach decompression postoperative and as a feeding tube to the patient with poor swallow ( mostly in patient who suffer from cerebrovascular accident.
The equipments requires are sterile gauze, lubricants, 50ml syringe, dressing pack, gallipots, disposable bowel, gloves, hypoallergenic tape, pH testing strips and 12 -18 French size nasogastric tube.
Before beginning the procedure there are few things that we need to know. There are few condition, where nasogastric tube insertion is contraindicated. The contraindications are nasal septum deviation, fractures of the base of the skull, stricture of the esophagus, tracheo esophageal fistula, obstructing tumor and achalasia cardia.
The first step is to explain the procedure to the patient. Nasogastric tube insertion is an uncomfortable procedure which may result in gagging.
Patient is position in a semi upright position.
Next, the length of the nasogastric tube require can be identify by measuring the distance from the bridge of the nose to the tip of the earlobe and then to the xiphoid process.
The patency of the nostril is assessed. the nasogastric tube is unwrap and tip of the nasogastric tube is lubricated with lubricating gel.
The tip of the nasogastric tube is insert into the nostril and later the nasogastric tube is advanced along the floor of the nasal cavity in the backward and downward direction.
Patient need to swallow as the nasogastric tube passed the nasopharynx. Patient may required to use straw or cup of water.
The nasogastric tube may need to be removed if the patient shows any signs of distress such as cyanosis or coughing and consider the other nostril.
After assuming that the the nasogastric tube has reached the stomach, perform test to confirm it. The test may include aspiration of the fluid using the syringe. Medication such as proton pump inhibitor should be avoided as it may elevate the pH can give a false negative result.
The aspirate is later tested with pH testing strip. If the pH id 5.5 or less, then it suggest that the nasogastric tube has reached the stomach .
The position of the nasogastric tube can also be confirmed by radiography of the chest highly recommended due to low pH fluid may be originated from the lung.
The internal wire of the tube should remain intact in this case. It is not recommended to auscultated the stomach to confirm the position of the nasogastric tube.
Once, the position of the nasogastric tube in the stomach is confirmed, ( if the tube is advanced by 55- 60 cm form the nostril then tip of the nasogastric tube is usually within the stomach) the internal wire is removed and the nasogastric tube is secured to the tip of the nose and curved the remainder of the tube over the ears and cheek.
The common complication associated with nasogastric tube insertion include perforation of the esophagus, malpositioning of the nasogastric tube to the lung and trauma to the cavities of the nasal or pharyngeal.
