Medicine Notes - Clinical Examination - Mitral Stenosis
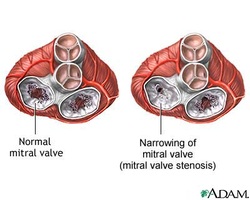
Mitral stenosis
The causes of rheumatic fever is commonly rheumatic fever.
The patient with mitral stenosis will present with malar flush. The pulse volume is low with irregular atrial fibrillation. The apex is tapping in nature and in normal position ( mid clavicular line at the fifth intercostal space). There will be palpable first heart sound and the present of parasternal heave. Mitral stenosis present with opening snap. There will be a mid diastolic murmur at the apex which is best heard with the bell of the stethoscope. The murmur is best heard while the patient in the left lateral position.
The common complications of mitral stenosis are hypotension, pulmonary hypertension and dyspnea. There is a high risk of developing embolisation . The patient should be treated with anticoagulation and consider valve replacement and ballon valvuloplasty.
The causes of rheumatic fever is commonly rheumatic fever.
The patient with mitral stenosis will present with malar flush. The pulse volume is low with irregular atrial fibrillation. The apex is tapping in nature and in normal position ( mid clavicular line at the fifth intercostal space). There will be palpable first heart sound and the present of parasternal heave. Mitral stenosis present with opening snap. There will be a mid diastolic murmur at the apex which is best heard with the bell of the stethoscope. The murmur is best heard while the patient in the left lateral position.
The common complications of mitral stenosis are hypotension, pulmonary hypertension and dyspnea. There is a high risk of developing embolisation . The patient should be treated with anticoagulation and consider valve replacement and ballon valvuloplasty.
