Symptom finder- The causes of hyperglycemia
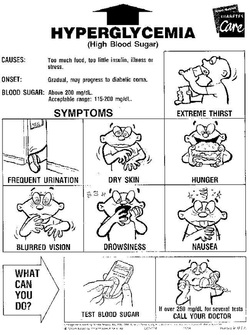
Symptom finder - The causes of hyperglycemia
Is hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus the same thing? Hyperglycemia is a biochemical condition when the plasma glucose is more than 7 mmol/l. Diabetes mellitus is the common causes of hyperglycemia. However, there are few more causes of hyperglycemia.
Other causes of hyperglycemia are pregnancy, Cushing’s syndrome, myocardial infarction, inflammation, stoke, infection, bulimia nervosa and drugs. Drugs causing diabetes mellitus are L- asparaginase, protease inhibitor, pentamidine, antipsychotic agent, niacin, thiazide diuretics, beta blockers and corticosteroids.
Hyperglycemia is presented as recurrent infection of the skin. Acute cases of hyperglycemia are presented with stupor, hyperventilation and coma ( part of diabetic ketoacidosis).Diabetic ketoacidosis is caused by poor glucose control and intercurrent infection. Diabetic ketoacidosis is identified as raise glucose level and the present of ketones and glucose in the urine . It is an emergency condition but may be the first presenting symptoms of diabetes.
Other symptoms of hyperglycemia are polyphagia, polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, fatigue and blurred vision.
Drugs such as steroids are associated with hyperglycemia. Patient may complain of symptoms and signs that are similar to Cushing’s syndrome such as buffalo hump, weight gain, moon face, increase in appetite, weakness, central obesity cataract and striae as well as hypertension.
The late stages of pregnancy is also associated with hyperglycemia. The binge phase of bulimia may also lead to hyperglycemia. This is due to the increase in caloric level. Patient with bulimia nervosa may present with oral trauma, tooth decay, swollen salivary glands and dehydration.
Hyperglycemia is associated with diabetes. Type 1 diabetes most commonly affect young people while type 2 diabetes mostly affect older generation and obese individuals. Charcot’s joint, neuropathy, boils,abscess, retinopathy and vascular disease are the common finding of the complication of diabetes.
Recent illness such as stoke and myocardial infarction are also associated with hyperglycemia. Look for any evidence of heart failure. Patient is assessed neurologically as he may develop upper motor neuron lesions due to stroke.
The investigations require are full blood count, urea and electrolytes, blood glucose, BM stix, oral glucose tolerance test, urinalysis, beta HCG, HbA1c and arterial blood gases.
Full blood count may reveal rise white cell count due to inflammation and infection. Diabetic nephropathy is suggested due to the raise creatinine and urea. Blood glucose and BM stix may reveal raise blood glucose level.Urinalysis is useful in detection of diabetic ketoacidosis. ( as raised ketone and glucose in the urine). Oral glucose tolerance test is also useful for detection of glucose. Beta HCG is performed in case the woman is pregnant. Arterial blood gases may reveal the present of diabetic ketoacidosis and HbAIc is raised in diabetes.
Is hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus the same thing? Hyperglycemia is a biochemical condition when the plasma glucose is more than 7 mmol/l. Diabetes mellitus is the common causes of hyperglycemia. However, there are few more causes of hyperglycemia.
Other causes of hyperglycemia are pregnancy, Cushing’s syndrome, myocardial infarction, inflammation, stoke, infection, bulimia nervosa and drugs. Drugs causing diabetes mellitus are L- asparaginase, protease inhibitor, pentamidine, antipsychotic agent, niacin, thiazide diuretics, beta blockers and corticosteroids.
Hyperglycemia is presented as recurrent infection of the skin. Acute cases of hyperglycemia are presented with stupor, hyperventilation and coma ( part of diabetic ketoacidosis).Diabetic ketoacidosis is caused by poor glucose control and intercurrent infection. Diabetic ketoacidosis is identified as raise glucose level and the present of ketones and glucose in the urine . It is an emergency condition but may be the first presenting symptoms of diabetes.
Other symptoms of hyperglycemia are polyphagia, polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, fatigue and blurred vision.
Drugs such as steroids are associated with hyperglycemia. Patient may complain of symptoms and signs that are similar to Cushing’s syndrome such as buffalo hump, weight gain, moon face, increase in appetite, weakness, central obesity cataract and striae as well as hypertension.
The late stages of pregnancy is also associated with hyperglycemia. The binge phase of bulimia may also lead to hyperglycemia. This is due to the increase in caloric level. Patient with bulimia nervosa may present with oral trauma, tooth decay, swollen salivary glands and dehydration.
Hyperglycemia is associated with diabetes. Type 1 diabetes most commonly affect young people while type 2 diabetes mostly affect older generation and obese individuals. Charcot’s joint, neuropathy, boils,abscess, retinopathy and vascular disease are the common finding of the complication of diabetes.
Recent illness such as stoke and myocardial infarction are also associated with hyperglycemia. Look for any evidence of heart failure. Patient is assessed neurologically as he may develop upper motor neuron lesions due to stroke.
The investigations require are full blood count, urea and electrolytes, blood glucose, BM stix, oral glucose tolerance test, urinalysis, beta HCG, HbA1c and arterial blood gases.
Full blood count may reveal rise white cell count due to inflammation and infection. Diabetic nephropathy is suggested due to the raise creatinine and urea. Blood glucose and BM stix may reveal raise blood glucose level.Urinalysis is useful in detection of diabetic ketoacidosis. ( as raised ketone and glucose in the urine). Oral glucose tolerance test is also useful for detection of glucose. Beta HCG is performed in case the woman is pregnant. Arterial blood gases may reveal the present of diabetic ketoacidosis and HbAIc is raised in diabetes.
