Pathology definition - Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis may present with rheumatoid nodule which is non tender, firm. The rheumatoid nodule is also known as subcutaneous nodule which consists of fibrinoid necrosis with macrophages, fibroblasts and lymphocytes.
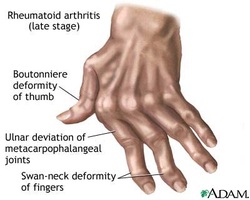
Patient with rheumatoid arthritis may present with symptoms and signs such as swan neck deformity which consists of flexion of distal interphalangeal joint and extension of the proximal interphalangeal joints.There will also be boutonniere deformity due to extension of the distal interphalangeal joint and flexion of the proximal interphalangeal joint. Patient may complain of symmetrical joint pain, swelling and stiffness that involved the proximal interphalangeal joint and distal interphalangeal joint. Mostly, the fingers, knee, wrist and ankle are affected. Patient will complain of stiffness mostly in the morning which improve with activity. There will also be ulnar deviation of the fingers.
Rheumatoid arthritis is caused mainly by patient with HLA-DR4. There will be lymphocytic infiltration and edematous synovium. There will be villi formation which composed of synovial lining cells. The synovial fluid may contain neutrophils. Pannus or fibrocellular granulation tissue may destroy and replace the cartilage. Joint deformity may occur finally.
There will be an increase in ESR and gamma globulins with the present of rheumatoid factor ( IgM antibody against IgG Fc fragment). The treatment will focus on immunosuppressant and NSAIDS.
Rheumatoid arthritis may present with rheumatoid nodule which is non tender, firm. The rheumatoid nodule is also known as subcutaneous nodule which consists of fibrinoid necrosis with macrophages, fibroblasts and lymphocytes.
Patient with rheumatoid arthritis may present with symptoms and signs such as swan neck deformity which consists of flexion of distal interphalangeal joint and extension of the proximal interphalangeal joints.There will also be boutonniere deformity due to extension of the distal interphalangeal joint and flexion of the proximal interphalangeal joint. Patient may complain of symmetrical joint pain, swelling and stiffness that involved the proximal interphalangeal joint and distal interphalangeal joint. Mostly, the fingers, knee, wrist and ankle are affected. Patient will complain of stiffness mostly in the morning which improve with activity. There will also be ulnar deviation of the fingers.
Rheumatoid arthritis is caused mainly by patient with HLA-DR4. There will be lymphocytic infiltration and edematous synovium. There will be villi formation which composed of synovial lining cells. The synovial fluid may contain neutrophils. Pannus or fibrocellular granulation tissue may destroy and replace the cartilage. Joint deformity may occur finally.
There will be an increase in ESR and gamma globulins with the present of rheumatoid factor ( IgM antibody against IgG Fc fragment). The treatment will focus on immunosuppressant and NSAIDS.
