Symptom finder - The causes of palpitation
Symptom finder - The causes of palpitation
Palpitation is caused by cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, atrial ectopic beats /premature atrial contraction and ventricular ectopic beats/premature ventricular contraction. Atrial fibrillation, ectopic atrial beats or ectopic ventricular beats are associated with irregular palpitation. Other causes of palpitation are ventricular tachycardia or supraventricular tachycardia. Supraventricular tachycardia is presented with chest pain, dizziness, breathlessness and sudden onset of tachycardia in teenager and childhood ( congenital anomaly).
Another causes of palpitation is sinus tachycardia. Sinus tachycardia is caused by alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, emotional stress and anxiety.
Palpitation is sometimes describes as skipping a beat, pounding or fluttering. Ideally , palpitation is an awareness of heartbeat. Palpitation may be associated with life - threatening disorders. However most cases of palpitation are benign.
It is important to distinguish the predisposing factors of palpitation, rate of and regularity of palpitations ( regular/irregular or fast/slow) and frequency of palpitation. In certain cases, palpitation may be radiated and felt at the neck. Always remember to ask the patient to tap the rhythm and rate of palpitation on the table. This is good and informative way.
Panic reaction or anxiety are commonly associated with normal manifestation of palpitation ( regular heart beat). Cardiac arrhythmias ( irregular heart rhythm / beat) is associated with palpitation. In certain cases of supraventricular tachycardia ( cardiac arrhythmias) may co exist with anxiety and panic attack.
Certain activities such as exercise , alcohol intake, smoking or caffeine may induced hypersecretion of catecholamines and precipitate arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia , atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia. Pathological heart condition such as hypertension and heart valve disease ( lead to atrial fibrillation), ischemic heart disease and heart failure ( lead to ventricular arrhythmias ) may cause palpitation.
Cardiac arrhythmias may occur in teenage years or childhood and this is always associated with congenital abnormalities.
Cardiac arrhythmias such as supraventricular tachycardia or ventricular tachycardia may present with syncope and dizziness.
Palpitation is caused by cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, atrial ectopic beats /premature atrial contraction and ventricular ectopic beats/premature ventricular contraction. Atrial fibrillation, ectopic atrial beats or ectopic ventricular beats are associated with irregular palpitation. Other causes of palpitation are ventricular tachycardia or supraventricular tachycardia. Supraventricular tachycardia is presented with chest pain, dizziness, breathlessness and sudden onset of tachycardia in teenager and childhood ( congenital anomaly).
Another causes of palpitation is sinus tachycardia. Sinus tachycardia is caused by alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, emotional stress and anxiety.
Palpitation is sometimes describes as skipping a beat, pounding or fluttering. Ideally , palpitation is an awareness of heartbeat. Palpitation may be associated with life - threatening disorders. However most cases of palpitation are benign.
It is important to distinguish the predisposing factors of palpitation, rate of and regularity of palpitations ( regular/irregular or fast/slow) and frequency of palpitation. In certain cases, palpitation may be radiated and felt at the neck. Always remember to ask the patient to tap the rhythm and rate of palpitation on the table. This is good and informative way.
Panic reaction or anxiety are commonly associated with normal manifestation of palpitation ( regular heart beat). Cardiac arrhythmias ( irregular heart rhythm / beat) is associated with palpitation. In certain cases of supraventricular tachycardia ( cardiac arrhythmias) may co exist with anxiety and panic attack.
Certain activities such as exercise , alcohol intake, smoking or caffeine may induced hypersecretion of catecholamines and precipitate arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia , atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia. Pathological heart condition such as hypertension and heart valve disease ( lead to atrial fibrillation), ischemic heart disease and heart failure ( lead to ventricular arrhythmias ) may cause palpitation.
Cardiac arrhythmias may occur in teenage years or childhood and this is always associated with congenital abnormalities.
Cardiac arrhythmias such as supraventricular tachycardia or ventricular tachycardia may present with syncope and dizziness.
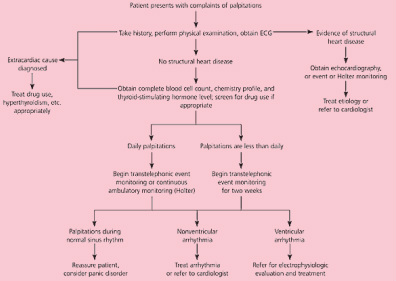
Physical examination is usually perform during the period of palpitation. The rate and rhythm of the pulse are notified.It is wise to auscultate the heart rate at the cardiac apex as in atrial fibrillation, not all beats are conducted in pulse. Auscultation is also important to identify any underlying heart disorder such as systolic click and systolic murmur due to mitral valve prolapse and that is associated with atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia.
The investigation requires is 12 led ECG. ECG is taken while the patient is resting. No arrhythmias are detected at this moment but the predisposing factors for arrhythmias can be detected. Short PR interval is indicated with less than 0.12 second . Short PR interval is due to the presence of accessory pathway that lead to supraventricular arrhythmias . ECG may also shoe the present of left ventricular hypertrophy that indicated the present of structural heart disease such as obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and hypertension. The present of changes in the ST segment or T wave abnormalities and Q wave are suggestive of ischemic heart disease.Ectopic beat such as ventricular or atrial premature contraction may also present on ECG.
Continuous ambulatory ECG monitoring is useful for identifying and detection of arrhythmia. Further investigation may reveal the present of ectopic beast ( ventricular or atrial premature beat). Sinus rhythm may also be identified. Only 7% of serious cases of arrhythmias are detected on ambulatory ECG monitoring.
Other investigations are only performed in patient with high risk of arrhythmias such as dizziness, structural heart disease, regular palpitations and family history of arrhythmias.
The investigation requires is 12 led ECG. ECG is taken while the patient is resting. No arrhythmias are detected at this moment but the predisposing factors for arrhythmias can be detected. Short PR interval is indicated with less than 0.12 second . Short PR interval is due to the presence of accessory pathway that lead to supraventricular arrhythmias . ECG may also shoe the present of left ventricular hypertrophy that indicated the present of structural heart disease such as obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and hypertension. The present of changes in the ST segment or T wave abnormalities and Q wave are suggestive of ischemic heart disease.Ectopic beat such as ventricular or atrial premature contraction may also present on ECG.
Continuous ambulatory ECG monitoring is useful for identifying and detection of arrhythmia. Further investigation may reveal the present of ectopic beast ( ventricular or atrial premature beat). Sinus rhythm may also be identified. Only 7% of serious cases of arrhythmias are detected on ambulatory ECG monitoring.
Other investigations are only performed in patient with high risk of arrhythmias such as dizziness, structural heart disease, regular palpitations and family history of arrhythmias.
