Pediatric Definition - Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is also known as acute lung injury.
The common causes of acute respiratory distress syndrome are sepsis, burns, trauma, shocks, pneumonia, drowning and inhalation injury.
Pathologically, there will be accumulation of extravascular lung water due to increase in the permeability of the capillary.
Patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome may present with dyspnea, respiratory alkalosis and tachypnea.
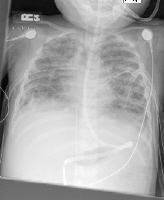
There will be evidence of bilateral pulmonary infiltration which indicates pulmonary edema. Patient may develop hypoxemia due to refractory reaction to supplemental oxygen.
The treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome may include ventilation ( high frequency oscillatory ventilation ).
Hemodynamic support is considered with proper fluid management to avoid pulmonary edema.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is also known as acute lung injury.
The common causes of acute respiratory distress syndrome are sepsis, burns, trauma, shocks, pneumonia, drowning and inhalation injury.
Pathologically, there will be accumulation of extravascular lung water due to increase in the permeability of the capillary.
Patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome may present with dyspnea, respiratory alkalosis and tachypnea.
There will be evidence of bilateral pulmonary infiltration which indicates pulmonary edema. Patient may develop hypoxemia due to refractory reaction to supplemental oxygen.
The treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome may include ventilation ( high frequency oscillatory ventilation ).
Hemodynamic support is considered with proper fluid management to avoid pulmonary edema.