Pathology definition - Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia Gravis
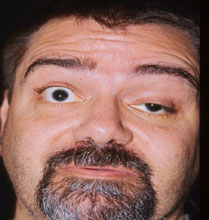
Myasthenia gravis initially present with diplopia or ptosis due to involvement of the extraocular muscle.Other presentations include weakness of the facial muscle and muscle of the extremities which are worsen with fatigue. Myasthenia gravis mostly affect female.
Myasthenia gravis occur due to infiltration of the complement factors and immune complex and loss of the acetylcholine receptors. The acetylcholine receptor will loss due to the action of antibodies directed against the acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. There will be a blockage of the synaptic transmission. Myasthenia gravis is associated with hyperplasia of the thymus and thymoma. It is important to perform thymectomy in this case. Other form of treatment may include anti cholinesterase, prednisolone and plasmapheresis.
Myasthenia gravis is detected by performing a test with administration of edrophonium.
Edrophonium is a short acting cholinesterase.
Myasthenia gravis initially present with diplopia or ptosis due to involvement of the extraocular muscle.Other presentations include weakness of the facial muscle and muscle of the extremities which are worsen with fatigue. Myasthenia gravis mostly affect female.
Myasthenia gravis occur due to infiltration of the complement factors and immune complex and loss of the acetylcholine receptors. The acetylcholine receptor will loss due to the action of antibodies directed against the acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. There will be a blockage of the synaptic transmission. Myasthenia gravis is associated with hyperplasia of the thymus and thymoma. It is important to perform thymectomy in this case. Other form of treatment may include anti cholinesterase, prednisolone and plasmapheresis.
Myasthenia gravis is detected by performing a test with administration of edrophonium.
Edrophonium is a short acting cholinesterase.
