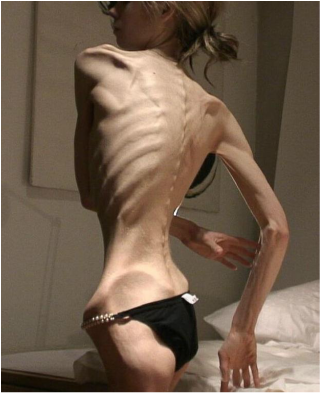
Pediatric Definition - Anorexia Nervosa
Anorexia Nervosa
The common differential diagnosis of anorexia nervosa are inflammatory bowel disease, HIV, celiac disease, hyperthyroidism, malignancy, depression and diabetes.
The symptoms and signs of anorexia nervosa may include bradycardia, reduction in body temperature, light - headedness, dizziness, syncope, cold feet, cold hands, lanugo, brittle nails, thinning hair, dry skin, constipation, early satiety, gastroesophageal reflux and amenorrhea.
The investigations may reveal increased AST, increased ALT, increased cholesterol, increased blood urea nitrogen and creatinine, decreased alkaline phosphatase, prolonged QT interval and decreased phosphorus as well as low TSH.
The common treatment of anorexia nervosa may include zinc supplementation, nutrition treatment, psychotherapy and symptomatic treatment for reflux and constipation.
The common differential diagnosis of anorexia nervosa are inflammatory bowel disease, HIV, celiac disease, hyperthyroidism, malignancy, depression and diabetes.
The symptoms and signs of anorexia nervosa may include bradycardia, reduction in body temperature, light - headedness, dizziness, syncope, cold feet, cold hands, lanugo, brittle nails, thinning hair, dry skin, constipation, early satiety, gastroesophageal reflux and amenorrhea.
The investigations may reveal increased AST, increased ALT, increased cholesterol, increased blood urea nitrogen and creatinine, decreased alkaline phosphatase, prolonged QT interval and decreased phosphorus as well as low TSH.
The common treatment of anorexia nervosa may include zinc supplementation, nutrition treatment, psychotherapy and symptomatic treatment for reflux and constipation.