Pathology definition - Barrett Esophagus
Barrett esophagus
Gastroesophageal reflux disease which is left untreated may lead to barrett esophagus. Barrett esophagus is one of the most common complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux.
Patient with Barrett esophagus may complain of symptoms such as heartburn , belching and regurgitation after meals. Patient also complain retrosternal heartburn and difficulty in swallowing or dysphagia.
As with gastroesophageal reflux disease, patient is treated with antacids, proton pump inhibitor and H2 receptor antagonist.
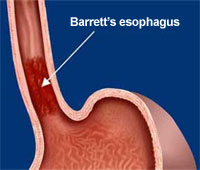
Pathologically, the normal squamous epithelium lining of the esophagus is being replaced with metaplastic columnar epithelium. The columnar cells may present as hyperchromatic and enlarged nuclei which is a common sign of dysplasia. Goblet cells and mucosal glands may also present with the metaplastic columnar epithelium. Endoscopy study may reveal a circumferential and tongue like projection of orange,gastric type epithelium from the stomach into distal tubular esophagus.
Barrett esophagus carries a higher risk of developing esophageal adenocarcinoma in the near future. Besides that Barrett esophagus may also lead to stricture erosive lesion and ulceration.
References
1.Aj, Cameron, and Carpenter Ha. “Barrett’s Esophagus, High-grade Dysplasia, and Early Adenocarcinoma: a Pathological Study.” The American Journal of Gastroenterology 92, no. 4 (April 1997): 586–591.
2.Shaheen N, and Ransohoff DF. “Gastroesophageal Reflux, Barrett Esophagus, and Esophageal Cancer: Scientific Review.” JAMA 287, no. 15 (April 17, 2002): 1972–1981. doi:10.1001/jama.287.15.1972.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease which is left untreated may lead to barrett esophagus. Barrett esophagus is one of the most common complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux.
Patient with Barrett esophagus may complain of symptoms such as heartburn , belching and regurgitation after meals. Patient also complain retrosternal heartburn and difficulty in swallowing or dysphagia.
As with gastroesophageal reflux disease, patient is treated with antacids, proton pump inhibitor and H2 receptor antagonist.
Pathologically, the normal squamous epithelium lining of the esophagus is being replaced with metaplastic columnar epithelium. The columnar cells may present as hyperchromatic and enlarged nuclei which is a common sign of dysplasia. Goblet cells and mucosal glands may also present with the metaplastic columnar epithelium. Endoscopy study may reveal a circumferential and tongue like projection of orange,gastric type epithelium from the stomach into distal tubular esophagus.
Barrett esophagus carries a higher risk of developing esophageal adenocarcinoma in the near future. Besides that Barrett esophagus may also lead to stricture erosive lesion and ulceration.
References
1.Aj, Cameron, and Carpenter Ha. “Barrett’s Esophagus, High-grade Dysplasia, and Early Adenocarcinoma: a Pathological Study.” The American Journal of Gastroenterology 92, no. 4 (April 1997): 586–591.
2.Shaheen N, and Ransohoff DF. “Gastroesophageal Reflux, Barrett Esophagus, and Esophageal Cancer: Scientific Review.” JAMA 287, no. 15 (April 17, 2002): 1972–1981. doi:10.1001/jama.287.15.1972.
