|
|
Pathology definition - Deep Vein Thrombosis
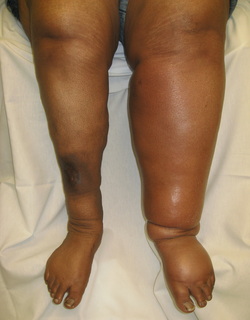
Deep vein thrombosis
The treatment option for deep vein thrombosis is with anticoagulation. In short term the treatment of deep vein thrombosis may include the intake of heparin while the long term treatment is with warfarin.
Deep vein thrombosis is associated with inflammation of the vein with the present of the venous thrombus which is attached to the wall of the vessel. The venous thrombus consists of pale gray fibrin strands and dark red in appearance.
Deep vein thrombosis is associated with Virchow triad which consists of venous stasis, hypercoagulability and injury to the endothelium.
Hypercoagulabilitiy commonly occur due to pregnancy, estrogen, myeloproliferative , cancer and protein S deficiency and protein C deficiency. Besides that factor V leiden may also lead to hypercoagulability. Factor V leiden is a mutation which alter the clotting factor V. The altered factor V will be inactivated by protein C. This will lead to hypercoagulability states.
Patient with deep vein thrombosis may complain of swelling of the calves as well as pain in the calves with palpable superficial vein.. In worst case, patient may present with venous insufficiency and pulmonary embolism. Homan sign is positive. Positive Homan sign is characterized by pain with dorsiflexion. There also will be a raise in the D dimer level.
References
1.Weinmann, Eran E., and Edwin W. Salzman. “Deep-Vein Thrombosis.” New England Journal of Medicine 331, no. 24 (December 15, 1994): 1630–1641. doi:10.1056/NEJM199412153312407.
2.Wells, Philip S., David R. Anderson, Marc Rodger, Melissa Forgie, Clive Kearon, Jonathan Dreyer, George Kovacs, Michael Mitchell, Bernard Lewandowski, and Michael J. Kovacs. “Evaluation of D-Dimer in the Diagnosis of Suspected Deep-Vein Thrombosis.” New England Journal of Medicine 349, no. 13 (2003): 1227–1235. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa023153.
The treatment option for deep vein thrombosis is with anticoagulation. In short term the treatment of deep vein thrombosis may include the intake of heparin while the long term treatment is with warfarin.
Deep vein thrombosis is associated with inflammation of the vein with the present of the venous thrombus which is attached to the wall of the vessel. The venous thrombus consists of pale gray fibrin strands and dark red in appearance.
Deep vein thrombosis is associated with Virchow triad which consists of venous stasis, hypercoagulability and injury to the endothelium.
Hypercoagulabilitiy commonly occur due to pregnancy, estrogen, myeloproliferative , cancer and protein S deficiency and protein C deficiency. Besides that factor V leiden may also lead to hypercoagulability. Factor V leiden is a mutation which alter the clotting factor V. The altered factor V will be inactivated by protein C. This will lead to hypercoagulability states.
Patient with deep vein thrombosis may complain of swelling of the calves as well as pain in the calves with palpable superficial vein.. In worst case, patient may present with venous insufficiency and pulmonary embolism. Homan sign is positive. Positive Homan sign is characterized by pain with dorsiflexion. There also will be a raise in the D dimer level.
References
1.Weinmann, Eran E., and Edwin W. Salzman. “Deep-Vein Thrombosis.” New England Journal of Medicine 331, no. 24 (December 15, 1994): 1630–1641. doi:10.1056/NEJM199412153312407.
2.Wells, Philip S., David R. Anderson, Marc Rodger, Melissa Forgie, Clive Kearon, Jonathan Dreyer, George Kovacs, Michael Mitchell, Bernard Lewandowski, and Michael J. Kovacs. “Evaluation of D-Dimer in the Diagnosis of Suspected Deep-Vein Thrombosis.” New England Journal of Medicine 349, no. 13 (2003): 1227–1235. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa023153.
