Pathology definition - Hashimoto Thyroiditis
Hashimoto Thyroiditis
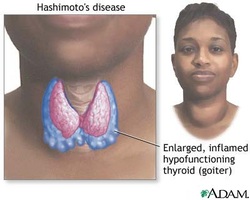
Hashimoto thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorders. Patient may present with diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland which is also known as goiter.
Hashimoto thyroiditis may present with symptoms and signs such as transient hyperthyroidism which is followed by hypothyroidism. Synthetic levothyroxine is the treatment choice for Hashimoto thyroiditis.
Patient with HLA - B5 and patient with HLA - DR 5 positive are more susceptible to develop Hashimoto thyroiditis besides, middle aged women and family history of other autoimmune diseases which may include Hashimoto thyroiditis itself.
Hashimoto thyroiditis may present with plasma cells and lymphocytic infiltrations of the thyroid gland with atrophic of the thyroid follicles and germinal center formation. There will be a present of the Hurthle cell. Hurthle cell is a collection of the epithelial cells and eosinophilic cytoplasm.
There will also be autoantibodies against iodine receptor, thyroid peroxidase, thyroglobulin and TSH receptor.
Hashimoto thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorders. Patient may present with diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland which is also known as goiter.
Hashimoto thyroiditis may present with symptoms and signs such as transient hyperthyroidism which is followed by hypothyroidism. Synthetic levothyroxine is the treatment choice for Hashimoto thyroiditis.
Patient with HLA - B5 and patient with HLA - DR 5 positive are more susceptible to develop Hashimoto thyroiditis besides, middle aged women and family history of other autoimmune diseases which may include Hashimoto thyroiditis itself.
Hashimoto thyroiditis may present with plasma cells and lymphocytic infiltrations of the thyroid gland with atrophic of the thyroid follicles and germinal center formation. There will be a present of the Hurthle cell. Hurthle cell is a collection of the epithelial cells and eosinophilic cytoplasm.
There will also be autoantibodies against iodine receptor, thyroid peroxidase, thyroglobulin and TSH receptor.
