|
|
Pathology definition - Mitral Regurgitation
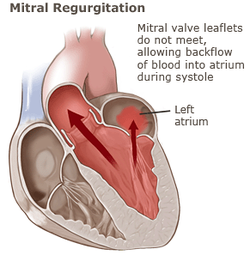
Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral regurgitation is also known as mitral incompetence/leakage of mitral valve.Patient typically complain of weakness and shortness of breath on exertion. Mitral regurgitation is associated with disruption and distortion of the normal alignment and structures of the mitral valve as well as the papillary muscle( due to the after effect of myocardial infarction). In worst case scenario, mitral regurgitation may lead to right ventricular heart failure and pulmonary hypertension.
Mitral regurgitation may lead to acute case of pulmonary edema. Mitral regurgitation may present with third heart sound, systolic v waves and pansystolic murmur at the apex which later radiated to the axilla.
The common causes of mitral regurgitation are mitral valve prolapse, left ventricular dilation, myocardial infarction, infective endocarditis and rheumatic heart disease.
The treatment of mitral regurgitation may include mitral valve replacement therapy as well as endocarditis prophylaxis.
References
1.Sanders, Charles A., et al. "Diagnosis and surgical treatment of mitral regurgitation secondary to ruptured chordae tendineae." New England Journal of Medicine 276.17 (1967): 943-949.
2.Piérard, Luc A., and Patrizio Lancellotti. "The role of ischemic mitral regurgitation in the pathogenesis of acute pulmonary edema." New England Journal of Medicine 351.16 (2004): 1627-1634.
Mitral regurgitation is also known as mitral incompetence/leakage of mitral valve.Patient typically complain of weakness and shortness of breath on exertion. Mitral regurgitation is associated with disruption and distortion of the normal alignment and structures of the mitral valve as well as the papillary muscle( due to the after effect of myocardial infarction). In worst case scenario, mitral regurgitation may lead to right ventricular heart failure and pulmonary hypertension.
Mitral regurgitation may lead to acute case of pulmonary edema. Mitral regurgitation may present with third heart sound, systolic v waves and pansystolic murmur at the apex which later radiated to the axilla.
The common causes of mitral regurgitation are mitral valve prolapse, left ventricular dilation, myocardial infarction, infective endocarditis and rheumatic heart disease.
The treatment of mitral regurgitation may include mitral valve replacement therapy as well as endocarditis prophylaxis.
References
1.Sanders, Charles A., et al. "Diagnosis and surgical treatment of mitral regurgitation secondary to ruptured chordae tendineae." New England Journal of Medicine 276.17 (1967): 943-949.
2.Piérard, Luc A., and Patrizio Lancellotti. "The role of ischemic mitral regurgitation in the pathogenesis of acute pulmonary edema." New England Journal of Medicine 351.16 (2004): 1627-1634.
