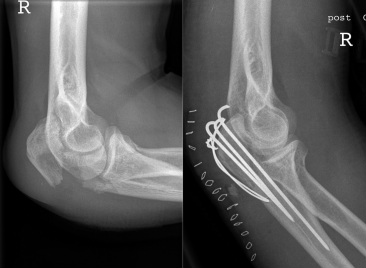
Olecranon fractures
Olecranon fracture
What is olecranon? Olecranon is the proximal projection of the bony component of the ulna of the elbow. Olecranon form the ulna humeral portion of the elbow elbow joint by articulating with the trochlea of the distal humerus. The articulations play a part in maintaining the extension and flexion of the elbow joint . Besides that, olecranon is also the insertion sites for the triceps tendon. The extension of the elbow is produced by the pulling of the olecranon from the contraction of the triceps. Arm function will be disrupted due to the fracture of the olecranon which affect the extensor component of the elbow. Post- traumatic arthritis may develop due to intra articular fracture which is not repaired.
Olecranon fracture can be classified based on its characteristic ( comminuted /simple. oblique/transverse, or displaced/non displaced) pr the amount of articular surface which involves in the olecranon notch such as type 1 olecranon fracture ( proximal 1/3 of the notch), type 2 olecranon fracture ( middle 1/3 of the notch) and type 3 olecranon fracture( distal 1/3 of the notch). Any sports mostly skating should be avoided or elbow pad may be required.
In term of epidemiology, olecranon fracture usually occur after a sport injury, fall or motor vehicle accident. Osteoporotic or elderly patient with history of loco- energy fall may sustain olecranon fracture. Olecranon fracture is more common to present in adult than in children. In children, this type of fracture is more likely to cause supracondylar fracture ( fracture of the distal humerus). Olecranon fracture is most commonly associated with direct blow to the tip of the elbow or fall on the outstretched hand while the elbow is in the flexing position. Olecranon fracture is associated with neurological damage such as radial, median and ulnar nerve damages, instability of the elbow, avulsion of the triceps, radial head fracture or elbow dislocation.
Patient will complain of swelling, pain , deformity and ecchymosis of the elbow. He may also has the trouble to extend the elbow. Elbow dislocation and radial head fracture are often associated with this injury. General examination should focus on the function of the ulnar and the radial nerves, the triceps muscle and the vascular status of the upper extremity. Defect is palpable on the posterior part of the elbow. Patient is asked to extend the elbow, against gravity to test the triceps mechanism integrity. Complete examination is performed to determine whether it is a closed or open fractures and to determine the extent of the soft injury.
The routine lab test is performed pre operatively depending on the patient ‘s age and general medical condition. Imaging technique may include radiography and CT scan.It is best to obtain lateral and AP radiography of the elbow. Any associated radial head injury is confirmed by getting the radiocapitellar view of the region.The differential diagnosis of olecranon fracture may include radial head fracture, dislocation of the elbow and distal humerus fracture.
The general treatment may include immobilization in an above the elbow splint or cast with flexion of the elbow in 90 degree for 4 weeks in case of non - displaced fracture . After 10 days of injury,follow up radiography is required to make sure the fracture is not displaced. Any fracture that is displaced required surgical fixation to restore and correct the function of the extensor mechanism. After developing a fracture , the affected arm should be splint 90 degree of fixation comfortably with a sling being offered. Patient is advised to move the shoulder and hand to prevent stiffness. Special care is required to maintain the personal hygiene in the underarm region and keep the splint in a comfortable position.
Physical therapy approaches may involve gentle passive ranges of movement and strengthening exercises to reduce the complication of olecranon fracture and prolonged immobilization. Active range of movement exercise is considered gradually if the fracture is healing and callus formation is seen based on the radiographic evidence. Ipsilateral hand and shoulder movement should also be encouraged. Analgesic is considered to relieve the pain after fracture.
Surgery is the main option in treating olecranon fracture which affect the mechanism of the extensor. The aim of repairing the fracture is to restore the surface of the joint. There are plenty of repair technique. The technique depends on the amount of comminuted fracture, the direction of the line of fracture and the sizes of the fragment. Non displaced and stable fractures should be treated non - operatively. Open reduction and fixation are requested for displaced fracture while open fractures require fixation and surgical debridement. Excision and repair are considered for small avulsion fractures. In this procedure, the tendon of the triceps are sutured back to the olecranon. Bony fixation should be considered as removal of the bone does increase joint pressure. A tension band wire and 2 Kiirschner wires are used to resists ant pulling of the triceps muscle in transverse fracture. Tension band wire and inter fragmentary screw fixation is useful in repairing any oblique fracture. Screw fixation appears to be stronger than tension band wires. Fixation with plating is required for any severely comminuted fractures which cannot be treated with tension wiring. A pre contoured plate or 3.5 mm reconstruction plate which can be bent is use to fit the olecranon. Bone grafting is required to repair any defect associated with bone loss due to fracture. After surgery has been competed, the arm need to be splinted while waiting for the skin to heal. This is follow by early range of motion exercise.
For more than 90% of the patient, prognosis is good. Worse outcome is associated with articular involvement with fracture.
The complication of olecranon fracture may include malunion, elbow arthritis, flexion contraction, ulnar neuropathy, radial neuropathy and non union. Radiography technique is useful to monitor the healing fracture and the strength of the arm and range of movement of the elbow should be monitored. Fracture will heal in 2- 3 months. For the next 3 months additional physical therapy is required to strengthen the arm.
What is olecranon? Olecranon is the proximal projection of the bony component of the ulna of the elbow. Olecranon form the ulna humeral portion of the elbow elbow joint by articulating with the trochlea of the distal humerus. The articulations play a part in maintaining the extension and flexion of the elbow joint . Besides that, olecranon is also the insertion sites for the triceps tendon. The extension of the elbow is produced by the pulling of the olecranon from the contraction of the triceps. Arm function will be disrupted due to the fracture of the olecranon which affect the extensor component of the elbow. Post- traumatic arthritis may develop due to intra articular fracture which is not repaired.
Olecranon fracture can be classified based on its characteristic ( comminuted /simple. oblique/transverse, or displaced/non displaced) pr the amount of articular surface which involves in the olecranon notch such as type 1 olecranon fracture ( proximal 1/3 of the notch), type 2 olecranon fracture ( middle 1/3 of the notch) and type 3 olecranon fracture( distal 1/3 of the notch). Any sports mostly skating should be avoided or elbow pad may be required.
In term of epidemiology, olecranon fracture usually occur after a sport injury, fall or motor vehicle accident. Osteoporotic or elderly patient with history of loco- energy fall may sustain olecranon fracture. Olecranon fracture is more common to present in adult than in children. In children, this type of fracture is more likely to cause supracondylar fracture ( fracture of the distal humerus). Olecranon fracture is most commonly associated with direct blow to the tip of the elbow or fall on the outstretched hand while the elbow is in the flexing position. Olecranon fracture is associated with neurological damage such as radial, median and ulnar nerve damages, instability of the elbow, avulsion of the triceps, radial head fracture or elbow dislocation.
Patient will complain of swelling, pain , deformity and ecchymosis of the elbow. He may also has the trouble to extend the elbow. Elbow dislocation and radial head fracture are often associated with this injury. General examination should focus on the function of the ulnar and the radial nerves, the triceps muscle and the vascular status of the upper extremity. Defect is palpable on the posterior part of the elbow. Patient is asked to extend the elbow, against gravity to test the triceps mechanism integrity. Complete examination is performed to determine whether it is a closed or open fractures and to determine the extent of the soft injury.
The routine lab test is performed pre operatively depending on the patient ‘s age and general medical condition. Imaging technique may include radiography and CT scan.It is best to obtain lateral and AP radiography of the elbow. Any associated radial head injury is confirmed by getting the radiocapitellar view of the region.The differential diagnosis of olecranon fracture may include radial head fracture, dislocation of the elbow and distal humerus fracture.
The general treatment may include immobilization in an above the elbow splint or cast with flexion of the elbow in 90 degree for 4 weeks in case of non - displaced fracture . After 10 days of injury,follow up radiography is required to make sure the fracture is not displaced. Any fracture that is displaced required surgical fixation to restore and correct the function of the extensor mechanism. After developing a fracture , the affected arm should be splint 90 degree of fixation comfortably with a sling being offered. Patient is advised to move the shoulder and hand to prevent stiffness. Special care is required to maintain the personal hygiene in the underarm region and keep the splint in a comfortable position.
Physical therapy approaches may involve gentle passive ranges of movement and strengthening exercises to reduce the complication of olecranon fracture and prolonged immobilization. Active range of movement exercise is considered gradually if the fracture is healing and callus formation is seen based on the radiographic evidence. Ipsilateral hand and shoulder movement should also be encouraged. Analgesic is considered to relieve the pain after fracture.
Surgery is the main option in treating olecranon fracture which affect the mechanism of the extensor. The aim of repairing the fracture is to restore the surface of the joint. There are plenty of repair technique. The technique depends on the amount of comminuted fracture, the direction of the line of fracture and the sizes of the fragment. Non displaced and stable fractures should be treated non - operatively. Open reduction and fixation are requested for displaced fracture while open fractures require fixation and surgical debridement. Excision and repair are considered for small avulsion fractures. In this procedure, the tendon of the triceps are sutured back to the olecranon. Bony fixation should be considered as removal of the bone does increase joint pressure. A tension band wire and 2 Kiirschner wires are used to resists ant pulling of the triceps muscle in transverse fracture. Tension band wire and inter fragmentary screw fixation is useful in repairing any oblique fracture. Screw fixation appears to be stronger than tension band wires. Fixation with plating is required for any severely comminuted fractures which cannot be treated with tension wiring. A pre contoured plate or 3.5 mm reconstruction plate which can be bent is use to fit the olecranon. Bone grafting is required to repair any defect associated with bone loss due to fracture. After surgery has been competed, the arm need to be splinted while waiting for the skin to heal. This is follow by early range of motion exercise.
For more than 90% of the patient, prognosis is good. Worse outcome is associated with articular involvement with fracture.
The complication of olecranon fracture may include malunion, elbow arthritis, flexion contraction, ulnar neuropathy, radial neuropathy and non union. Radiography technique is useful to monitor the healing fracture and the strength of the arm and range of movement of the elbow should be monitored. Fracture will heal in 2- 3 months. For the next 3 months additional physical therapy is required to strengthen the arm.