Pathology definition - Metabolic Acidosis
Metabolic acidosis
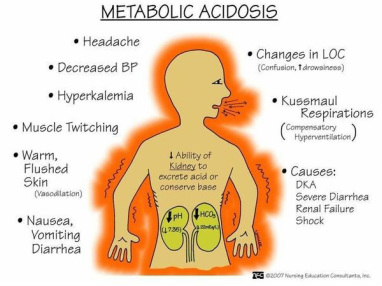
Patient with metabolic acidosis may present with deep, sighing respiration ( Kussmaul breathing), hyperventilation shock and hypotension. Metabolic acidosis may present with decreased in the hydrogen bicarbonate ion concentration with compensatory mechanism which lead to decrease in the partial pressure of the carbon dioxide. The pH will be decreased in metabolic acidosis.
Metabolic acidosis may lead to dilation of the vascular bed with decrease in the contraction of the myocardium.
Metabolic acidosis is divided into normal anion gap metabolic acidosis and anion gap metabolic acidosis. Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis is associated with renal tubular acidosis, overdose of acetazolamide and diarrhea.
Anion gap metabolic acidosis is associated with diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, renal failure, methanol and salicylate overdose. Metabolic acidosis is treated with bicarbonate.
Patient with metabolic acidosis may present with deep, sighing respiration ( Kussmaul breathing), hyperventilation shock and hypotension. Metabolic acidosis may present with decreased in the hydrogen bicarbonate ion concentration with compensatory mechanism which lead to decrease in the partial pressure of the carbon dioxide. The pH will be decreased in metabolic acidosis.
Metabolic acidosis may lead to dilation of the vascular bed with decrease in the contraction of the myocardium.
Metabolic acidosis is divided into normal anion gap metabolic acidosis and anion gap metabolic acidosis. Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis is associated with renal tubular acidosis, overdose of acetazolamide and diarrhea.
Anion gap metabolic acidosis is associated with diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, renal failure, methanol and salicylate overdose. Metabolic acidosis is treated with bicarbonate.
