Pathology definition - Down Syndrome
Down syndrome
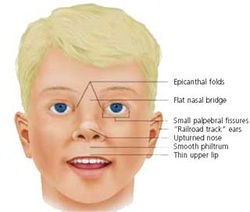
The common symptoms and signs of Down syndrome include, mental retardation, flat face, wide set eyes, short hands, simian crease, esophageal and duodenal atresia ( can be treated surgically) , brushfield spot, congenital defect of the heart, AV malformation, ventricular septal defect and ostium primum atrial septal defect.
Down syndrome is associated with trisomy 21. Trisomy 21 is associated with meiotic non disjunction. The incidence of developing trisomy 21 increase with maternal age. Down syndrome is also associated with Robertsonian translocation. The long arm of chromosome 21 is translocated into chromosome 14 or chromosome 22. Mosaicism due to mitotic non disjunction in chromosome 21 is also associated with Down syndrome.
The common complication of Down syndrome include increase susceptibility to infection, acute leukemia and degenerative changes of the brain like early onset of Alzheimer disease.
