Pathology definition - Prolactinoma
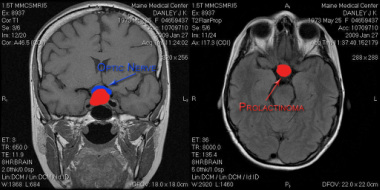
Prolactinoma
Patient with prolactinoma may present with visual disturbance / bitemporal hemianopia due to compression of the optic chiasm. Other signs of prolactinoma may also also include galactorrhea and fertility problem such as impotence in men or amenorrhea in women.
Prolactinoma may be treated with dopamine analog such as bromocriptine which will suppress the secretion of prolactin. Other treatment may include radiation and surgical removal of the pituitary adenoma.
Prolactinoma may be caused by pituitary adenoma or also known as pituitary lactotroph adenoma. Pituitary adenoma consists of multiple chromophobic cells with prolactin containing secretory granules.There will be an increase in the secretion of the prolactin / hyperprolactinoma which later also lead to decreased in the LH and FSH level. Pituitary adenoma is the most common in pituitary tumor.
There are other causes of hyperprolactinoma which may include renal insufficiency, methyl dopa intake ( disruption in the dopamine secretion), lesion on the hypothalamus and estrogen therapy.
Patient with prolactinoma may present with visual disturbance / bitemporal hemianopia due to compression of the optic chiasm. Other signs of prolactinoma may also also include galactorrhea and fertility problem such as impotence in men or amenorrhea in women.
Prolactinoma may be treated with dopamine analog such as bromocriptine which will suppress the secretion of prolactin. Other treatment may include radiation and surgical removal of the pituitary adenoma.
Prolactinoma may be caused by pituitary adenoma or also known as pituitary lactotroph adenoma. Pituitary adenoma consists of multiple chromophobic cells with prolactin containing secretory granules.There will be an increase in the secretion of the prolactin / hyperprolactinoma which later also lead to decreased in the LH and FSH level. Pituitary adenoma is the most common in pituitary tumor.
There are other causes of hyperprolactinoma which may include renal insufficiency, methyl dopa intake ( disruption in the dopamine secretion), lesion on the hypothalamus and estrogen therapy.
