Pathology definition - Multinodular Goiter
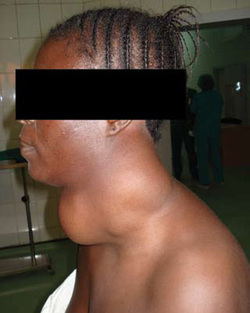
Multinodular goiter
Multinodular goiter may occur due to progression of simple goiter due to deficiency of the iodine, the effects of the goitrogens or deficiency in the thyroid hormone enzyme synthesis.
Patient with multinodular goiter may appear to be euthyroid and hyperthyroidism. On examination, patient may present with asymmetrical large nodules of the thyroid gland.
Patient may also complain of difficulty in swallowing ( dysphagia) and hoarseness of the voice due to local compression of the surrounding structure. Individual nodules of the multinodular goiter may appear with colloid rich follicles. There will be hyperplasia of the follicular epithelium, fibrosis, calcification and hemorrhages.
Multinodular goiter is treated with synthetic levothyroxine in case the patient euthyroid as it suppress the thyroid stimulating hormone levels .
Multinodular goiter may occur due to progression of simple goiter due to deficiency of the iodine, the effects of the goitrogens or deficiency in the thyroid hormone enzyme synthesis.
Patient with multinodular goiter may appear to be euthyroid and hyperthyroidism. On examination, patient may present with asymmetrical large nodules of the thyroid gland.
Patient may also complain of difficulty in swallowing ( dysphagia) and hoarseness of the voice due to local compression of the surrounding structure. Individual nodules of the multinodular goiter may appear with colloid rich follicles. There will be hyperplasia of the follicular epithelium, fibrosis, calcification and hemorrhages.
Multinodular goiter is treated with synthetic levothyroxine in case the patient euthyroid as it suppress the thyroid stimulating hormone levels .
