|
|
|
Emergency Strategy - How to clean an open wound
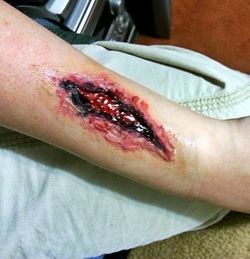
Emergency Strategy - How to clean an open wound
The initial steps include the assessment of the patient ‘s airway, breathing, circulation,disability and exposure. In case of open wound we also need to focus on other factors such as the present of open fractures, loss of tissue, contamination, damage to the nerve, vascular or rupture of the tendon, compartment syndrome and depth of the wound and area of the wound. The next step is to consider photographing the sites of the wound. Any gross contamination need to be removed by forceps. The sizes of the wound is identified by using the ruler.
The wound need to be cleaned with copious amount of normal saline irrigation ( avoiding high pressure irrigation as it may push the debris further)from the central outward to prevent further contamination. The wound also can be cleaned using the antiseptic. The joints need to be moved at the sites above and below the sites of injury with the aim to not miss any injuries to the tendon which can be easily missed in cases of the wound which incurred in different position. This happen in clinched fist injury.
The dead tissue need to be cut. Forceps and wound retraction is useful to monitor and examine the area of the wounds. Any damage to the tendons, nerves and wound will require further evaluation. These includes, rupture of the tendons, open fractures of the joints, compromise of the vascular system and injury to the nerve.
Besides, photography and visual assessment, x ray is also important as well as deep palpation in identifying contaminants ( glass or metal) and other injuries to the tissue that may be missed.
The swabs of the wound can be taken for microbiological studies.
Any cavity may present as a result of the wound and this cavity need to be drained. There are two options either using a wick ( emergency setting) or using the drain.
Insertion of the drain may involve identification of the dependent part of the wound cavity. the depth of the tract is identified by using artery forceps. In case of deep tract of the wound, the wound will require to be extended into the skin above the sites of the wound to allow the drainage to be performed effectively.
The corrugated drain is lated fit into the drain. Scissor is useful to cut and taper the drain. The tip of the forceps need to be pass from the base of the tract to make it visible form the surface of the skin. Incision is later made over the site of the forceps so that the drain can be inserted. The tip of the drain is grasp with the forceps. A loose suture is useful to prevent further dislodging of the drain. The loose suture is sutured into the skin around the drain or through one of the corrugation of the drains. Besides that a loose suture is also useful to placed the pack in place while maintaining the opening of the small tract to allow drainage. Antiseptic solution is useful to wash and cleaned the wound.
The wound need to be dressed with a non stick dressing over the edges of the wound and the wound itself. besides dressing, bandage , tap and gauge is also needed. 48 - 96 hours later , wound inspection and debridement may be required. However, it will be earlier in case of wound contamination.
In case of superficial wound, the wound can be closed with interrupted non absorbable sutures only if the superficial wound is not contaminated. Skin glue may be useful in cases where superficial wound just involve the head and the face.
The equipment may require may include swabs, scissors, gloves, sterile drapes, local anesthetic, syringe, kidney dish, forceps, normal saline, antiseptic solution and scalpel.
Digital nerve block should be avoided in cases of laceration of the finger in case of causing an occlusion of the end artery which later lead to infarction of the digits
The common complication of wound cleaning include infection. Contaminated wounds should not be sutured close due to risk of infection which require further drainage.Bleeding, scar and further treatment/ surgical procedure may happen as part of the complication.
References
1.Molony, Darren. “Adrenaline-Induced Digital Ischaemia Reversed with Phentolamine.” ANZ Journal of Surgery 76, no. 12 (2006): 1125–1126. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.2006.03954.x.
2.Haury, Beth, George Rodeheaver, JoAnn Vensko, Milton T. Edgerton, and Richard F. Edlich. “Debridement: An Essential Component of Traumatic Wound Care.” The American Journal of Surgery 135, no. 2 (February 1978): 238–242. doi:10.1016/0002-9610(78)90108-3.
3.Atiyeh, B.S., J. Ioannovich, C.A. Al-Amm, and K.A. El-Musa. “Management of Acute and Chronic Open Wounds: The Importance of Moist Environment in Optimal Wound Healing.” Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 3, no. 3 (September 1, 2002): 179–195. doi:10.2174/1389201023378283.
The initial steps include the assessment of the patient ‘s airway, breathing, circulation,disability and exposure. In case of open wound we also need to focus on other factors such as the present of open fractures, loss of tissue, contamination, damage to the nerve, vascular or rupture of the tendon, compartment syndrome and depth of the wound and area of the wound. The next step is to consider photographing the sites of the wound. Any gross contamination need to be removed by forceps. The sizes of the wound is identified by using the ruler.
The wound need to be cleaned with copious amount of normal saline irrigation ( avoiding high pressure irrigation as it may push the debris further)from the central outward to prevent further contamination. The wound also can be cleaned using the antiseptic. The joints need to be moved at the sites above and below the sites of injury with the aim to not miss any injuries to the tendon which can be easily missed in cases of the wound which incurred in different position. This happen in clinched fist injury.
The dead tissue need to be cut. Forceps and wound retraction is useful to monitor and examine the area of the wounds. Any damage to the tendons, nerves and wound will require further evaluation. These includes, rupture of the tendons, open fractures of the joints, compromise of the vascular system and injury to the nerve.
Besides, photography and visual assessment, x ray is also important as well as deep palpation in identifying contaminants ( glass or metal) and other injuries to the tissue that may be missed.
The swabs of the wound can be taken for microbiological studies.
Any cavity may present as a result of the wound and this cavity need to be drained. There are two options either using a wick ( emergency setting) or using the drain.
Insertion of the drain may involve identification of the dependent part of the wound cavity. the depth of the tract is identified by using artery forceps. In case of deep tract of the wound, the wound will require to be extended into the skin above the sites of the wound to allow the drainage to be performed effectively.
The corrugated drain is lated fit into the drain. Scissor is useful to cut and taper the drain. The tip of the forceps need to be pass from the base of the tract to make it visible form the surface of the skin. Incision is later made over the site of the forceps so that the drain can be inserted. The tip of the drain is grasp with the forceps. A loose suture is useful to prevent further dislodging of the drain. The loose suture is sutured into the skin around the drain or through one of the corrugation of the drains. Besides that a loose suture is also useful to placed the pack in place while maintaining the opening of the small tract to allow drainage. Antiseptic solution is useful to wash and cleaned the wound.
The wound need to be dressed with a non stick dressing over the edges of the wound and the wound itself. besides dressing, bandage , tap and gauge is also needed. 48 - 96 hours later , wound inspection and debridement may be required. However, it will be earlier in case of wound contamination.
In case of superficial wound, the wound can be closed with interrupted non absorbable sutures only if the superficial wound is not contaminated. Skin glue may be useful in cases where superficial wound just involve the head and the face.
The equipment may require may include swabs, scissors, gloves, sterile drapes, local anesthetic, syringe, kidney dish, forceps, normal saline, antiseptic solution and scalpel.
Digital nerve block should be avoided in cases of laceration of the finger in case of causing an occlusion of the end artery which later lead to infarction of the digits
The common complication of wound cleaning include infection. Contaminated wounds should not be sutured close due to risk of infection which require further drainage.Bleeding, scar and further treatment/ surgical procedure may happen as part of the complication.
References
1.Molony, Darren. “Adrenaline-Induced Digital Ischaemia Reversed with Phentolamine.” ANZ Journal of Surgery 76, no. 12 (2006): 1125–1126. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.2006.03954.x.
2.Haury, Beth, George Rodeheaver, JoAnn Vensko, Milton T. Edgerton, and Richard F. Edlich. “Debridement: An Essential Component of Traumatic Wound Care.” The American Journal of Surgery 135, no. 2 (February 1978): 238–242. doi:10.1016/0002-9610(78)90108-3.
3.Atiyeh, B.S., J. Ioannovich, C.A. Al-Amm, and K.A. El-Musa. “Management of Acute and Chronic Open Wounds: The Importance of Moist Environment in Optimal Wound Healing.” Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 3, no. 3 (September 1, 2002): 179–195. doi:10.2174/1389201023378283.
