|
|
Pathology definition - Acute Rheumatic Fever
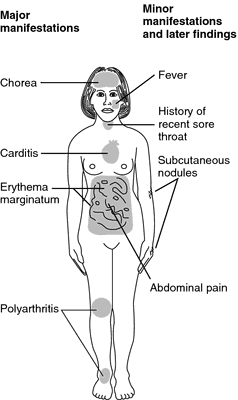 major Jones criteria
minor Jones criteria
major Jones criteria
minor Jones criteria
Acute rheumatic fever
Acute rheumatic fever may present with major Jones criteria and minor Jones criteria. Major Jones criteria include migratory polyarthritis, chorea, carditis, subcutaneous nodules and erythema marginatum. Minor Jones criteria include arthralgia, fever and previous streptococcal infection ( anti streptolysin O titer).
Acute rheumatic fever may occur 3 weeks after streptococcal pharyngitis infection. Acute rheumatic fever may lead to formation of antibodies against the group A, beta hemolytic streptococci which cross react with the tissue.
There will be Anitschkow cells and Aschoff bodies present in acute rheumatic fever. Anitschkow cells are multinucleated macrophages while Aschoff bodies are lymphocytes which is surrounded by inflammatory foci.
Acute rheumatic fever is commonly affecting children. The treatment will focus on salicylate, penicillin and benzathine penicillin (endocarditis prophylaxis).
One of the complication of acute rheumatic fever with rheumatic heart disease. Rheumatic heart disease may be develop 10 -20 years later after acute rheumatic fever, Rheumatic heart disease will affect the valves of the heart. Patient with rheumatic heart disease may present with mitral stenosis and aortic stenosis . The common complication of rheumatic heart disease are arrhythmias,ventricular hypertrophy and cardiac failure.
References
1.Carapetis, Jonathan R., Malcolm McDonald, and Nigel J. Wilson. "Acute rheumatic fever." The Lancet 366.9480 (2005): 155-168.
2.Marijon, Eloi, et al. "Rheumatic heart disease." The Lancet 379.9819 (2012): 953-964.
Acute rheumatic fever may present with major Jones criteria and minor Jones criteria. Major Jones criteria include migratory polyarthritis, chorea, carditis, subcutaneous nodules and erythema marginatum. Minor Jones criteria include arthralgia, fever and previous streptococcal infection ( anti streptolysin O titer).
Acute rheumatic fever may occur 3 weeks after streptococcal pharyngitis infection. Acute rheumatic fever may lead to formation of antibodies against the group A, beta hemolytic streptococci which cross react with the tissue.
There will be Anitschkow cells and Aschoff bodies present in acute rheumatic fever. Anitschkow cells are multinucleated macrophages while Aschoff bodies are lymphocytes which is surrounded by inflammatory foci.
Acute rheumatic fever is commonly affecting children. The treatment will focus on salicylate, penicillin and benzathine penicillin (endocarditis prophylaxis).
One of the complication of acute rheumatic fever with rheumatic heart disease. Rheumatic heart disease may be develop 10 -20 years later after acute rheumatic fever, Rheumatic heart disease will affect the valves of the heart. Patient with rheumatic heart disease may present with mitral stenosis and aortic stenosis . The common complication of rheumatic heart disease are arrhythmias,ventricular hypertrophy and cardiac failure.
References
1.Carapetis, Jonathan R., Malcolm McDonald, and Nigel J. Wilson. "Acute rheumatic fever." The Lancet 366.9480 (2005): 155-168.
2.Marijon, Eloi, et al. "Rheumatic heart disease." The Lancet 379.9819 (2012): 953-964.
