Pathology definition - Carcinoma Of The Vagina
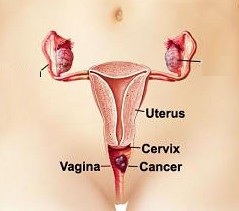
Carcinoma of the vagina
There are two forms of carcinoma of the vagina. These include clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina and the squamous cell carcinoma.
Clear cell adenocarcinoma may present with initially by vaginal adenosis which is a mucosal columnar epithelial lined gland that lined the areas normally occupied by stratified squamous epithelium. Later, there will be vacuolated glycogen containing cells present on the vagina.Mostly the clear cell adenocarcinoma may present as red granular lesion. This red granular lesion may present on the upper anterior part of the vagina.
Patient with clear cell adenocarcinoma may present with insidious signs of vaginal bleeding while remain asymptomatic throughout the course of the disorders.
Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina is mostly seen in children ( daughter) of the mother who receive DES therapy during the period of pregnancy. The treatment will focus on surgical removal of the clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina which later include radiotherapy treatment.
Another form of carcinoma of the vagina is known as squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina may present with plaque like mass in the upper posterior part of the vagina.There will be an epithelial thickening with dysplastic changes which later undergoes transformation into squamous cell carcinoma ( invasive in nature) with keratinization.
Patient may remain asymptomatic or present with leukorrhea or vaginal discharge with irregular spotting. Squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina is associated with patient who suffer from human papilloma virus infection.
The treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina may focus on surgical removal of the tumor and radiotherapy.
There are two forms of carcinoma of the vagina. These include clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina and the squamous cell carcinoma.
Clear cell adenocarcinoma may present with initially by vaginal adenosis which is a mucosal columnar epithelial lined gland that lined the areas normally occupied by stratified squamous epithelium. Later, there will be vacuolated glycogen containing cells present on the vagina.Mostly the clear cell adenocarcinoma may present as red granular lesion. This red granular lesion may present on the upper anterior part of the vagina.
Patient with clear cell adenocarcinoma may present with insidious signs of vaginal bleeding while remain asymptomatic throughout the course of the disorders.
Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina is mostly seen in children ( daughter) of the mother who receive DES therapy during the period of pregnancy. The treatment will focus on surgical removal of the clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina which later include radiotherapy treatment.
Another form of carcinoma of the vagina is known as squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina may present with plaque like mass in the upper posterior part of the vagina.There will be an epithelial thickening with dysplastic changes which later undergoes transformation into squamous cell carcinoma ( invasive in nature) with keratinization.
Patient may remain asymptomatic or present with leukorrhea or vaginal discharge with irregular spotting. Squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina is associated with patient who suffer from human papilloma virus infection.
The treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina may focus on surgical removal of the tumor and radiotherapy.
