Abscess Symptoms - Lung Abscess
Lung Abscess
Lung abscess is also known as pulmonary abscess.
A lung abscess is an infection of the lung parenchyma resulting in a necrotic cavity containing pus.
Lung abscess may be primary or secondary. Primary lung abscess refers to infection from
normal host organisms within the lung (e.g.,aspiration, pneumonia).
Secondary lung abscess results from other preexisting conditions (e.g., endocarditis, underlying lung cancer, pulmonary emboli).
Lung abscess may also be acute or chronic.Acute lung abscess is present if symptoms
are of less than 4 to 6 wk. Chronic lung abscess is present if symptoms last longer than 6 wk.
The risk factors of lung abscess are alcohol-related problems,seizure disorders cerebrovascular disorders with dysphagia, drug abuse,esophageal disorders (e.g., scleroderma,esophageal carcinoma, etc.), poor oral hygiene, obstructive malignant lung disease and bronchiectasis.
The most important factor predisposing to lung abscess is aspiration. Following aspiration as a major predisposing factor is periodontal disease.
Lung abscess is rare in an edentulous person. Approximately 90% of lung abscesses are
caused by anaerobic microorganisms (Bacteroides fragilis, Fusobacterium nucleatum, peptostreptococci, microaerophilic streptococci).
Pulmonary actinomycosis will also generate lung abscess. In most cases anaerobic infection is mixed with aerobic or facultative anaerobic organisms (S. aureus, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa).
Parasitic organisms including Paragonimus westermani and Entamoeba histolytica will also caused lung abscess. Fungi including Aspergillus, Cryptococcus,
Histoplasma, Blastomyces, and Coccidioides spp. commonly caused lung abscess.
Immunocompromised hosts may become infected with Aspergillus, mycobacteria, Nocardia, Legionella micdadei, and Rhodococcus equi.
The symptoms and signs of lung abscess are fever, chills, and sweats, cough, sputum production (purulent with foul odor),pleuritic chest pain,hemoptysis,dyspnea, malaise, fatigue, and weakness, tachycardia and tachypnea,dullness to percussion, whispered pectoriloquy,and bronchophony. Amphoric breath sounds (low-pitched sound
of air moving across a large open cavity).
The differential diagnosis of lung abscess is almost similar to lung cavitation related infection caused by bacterial (anaerobic, aerobic, infected bulla,
empyema, actinomycosis, tuberculosis), fungal (histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis,
blastomycosis, aspergillosis, cryptococcosis) and parasitic (amebiasis, echinococcosis) or malignancy (primary lung carcinoma, metastatic lung disease, lymphoma, Hodgkin’s
disease) and Wegener’s granulomatosis, sarcoidosis, endocarditis,
and septic pulmonary emboli.
The laboratory investigation required are full blood count with evidence of leukocytosis.Bacteriologic studies may include sputum Gram stain and culture (commonly
contaminated by oral flora), percutaneous transtracheal aspiration,percutaneous transthoracic aspiration ,fiberoptic bronchoscopy using bronchial brushings or bronchoalveolar lavage is the most widely used intervention when trying to obtain diagnostic bacteriologic cultures and blood cultures on some occasions (,30%)
may be positive.
If an empyema is present, obtaining empyema fluid via thoracentesis may isolate the
organism.
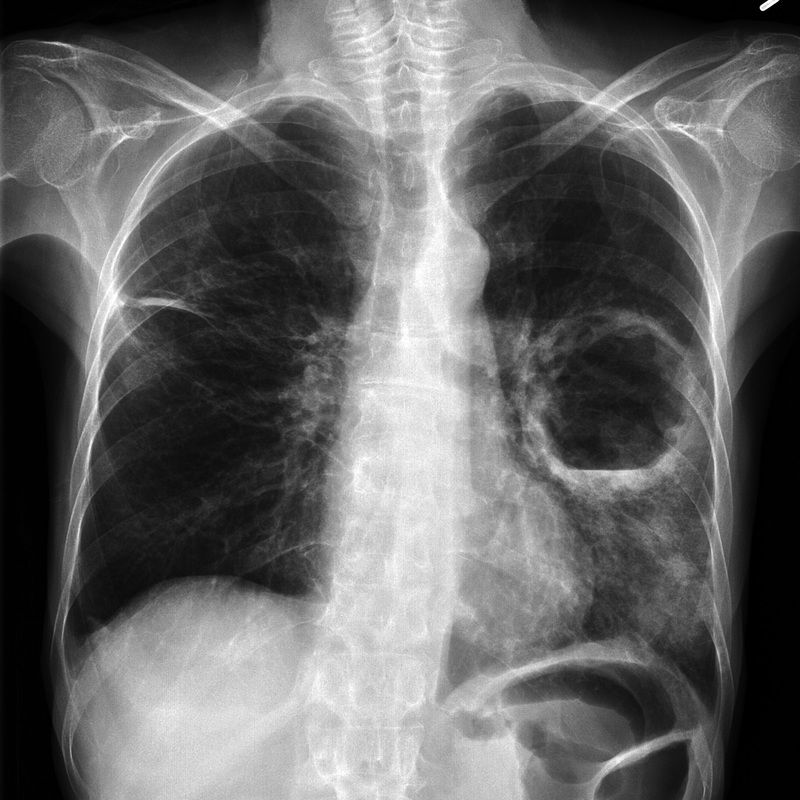
Chest x-ray makes the diagnosis of lung abscess showing the cavitary lesion with an air
fluid level. Lung abscesses are most commonly found in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe. Chest CT scan can localize and size the lesion and assist in differentiating lung abscesses from other pathologic processes (e.g., tumor, empyema, infected bulla,).
The treatment of lung abscess are oxygen therapy, respiratory therapy maneuver and postural drainage. Antibiotic treatment is also considered.
Bronchoscopy to assist with drainage and/or diagnosis is indicated in patients who fail to
respond to antibiotics or if there is suspected underlying malignancy.
Surgery is indicated on rare occasions (,10%) in patients with complications of
lung abscess.Complication of lung abscess are empyema, brain abscess, bronchiectasis, bronchopleural fistula and hepatobronchial fistula.
Lung abscess is also known as pulmonary abscess.
A lung abscess is an infection of the lung parenchyma resulting in a necrotic cavity containing pus.
Lung abscess may be primary or secondary. Primary lung abscess refers to infection from
normal host organisms within the lung (e.g.,aspiration, pneumonia).
Secondary lung abscess results from other preexisting conditions (e.g., endocarditis, underlying lung cancer, pulmonary emboli).
Lung abscess may also be acute or chronic.Acute lung abscess is present if symptoms
are of less than 4 to 6 wk. Chronic lung abscess is present if symptoms last longer than 6 wk.
The risk factors of lung abscess are alcohol-related problems,seizure disorders cerebrovascular disorders with dysphagia, drug abuse,esophageal disorders (e.g., scleroderma,esophageal carcinoma, etc.), poor oral hygiene, obstructive malignant lung disease and bronchiectasis.
The most important factor predisposing to lung abscess is aspiration. Following aspiration as a major predisposing factor is periodontal disease.
Lung abscess is rare in an edentulous person. Approximately 90% of lung abscesses are
caused by anaerobic microorganisms (Bacteroides fragilis, Fusobacterium nucleatum, peptostreptococci, microaerophilic streptococci).
Pulmonary actinomycosis will also generate lung abscess. In most cases anaerobic infection is mixed with aerobic or facultative anaerobic organisms (S. aureus, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa).
Parasitic organisms including Paragonimus westermani and Entamoeba histolytica will also caused lung abscess. Fungi including Aspergillus, Cryptococcus,
Histoplasma, Blastomyces, and Coccidioides spp. commonly caused lung abscess.
Immunocompromised hosts may become infected with Aspergillus, mycobacteria, Nocardia, Legionella micdadei, and Rhodococcus equi.
The symptoms and signs of lung abscess are fever, chills, and sweats, cough, sputum production (purulent with foul odor),pleuritic chest pain,hemoptysis,dyspnea, malaise, fatigue, and weakness, tachycardia and tachypnea,dullness to percussion, whispered pectoriloquy,and bronchophony. Amphoric breath sounds (low-pitched sound
of air moving across a large open cavity).
The differential diagnosis of lung abscess is almost similar to lung cavitation related infection caused by bacterial (anaerobic, aerobic, infected bulla,
empyema, actinomycosis, tuberculosis), fungal (histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis,
blastomycosis, aspergillosis, cryptococcosis) and parasitic (amebiasis, echinococcosis) or malignancy (primary lung carcinoma, metastatic lung disease, lymphoma, Hodgkin’s
disease) and Wegener’s granulomatosis, sarcoidosis, endocarditis,
and septic pulmonary emboli.
The laboratory investigation required are full blood count with evidence of leukocytosis.Bacteriologic studies may include sputum Gram stain and culture (commonly
contaminated by oral flora), percutaneous transtracheal aspiration,percutaneous transthoracic aspiration ,fiberoptic bronchoscopy using bronchial brushings or bronchoalveolar lavage is the most widely used intervention when trying to obtain diagnostic bacteriologic cultures and blood cultures on some occasions (,30%)
may be positive.
If an empyema is present, obtaining empyema fluid via thoracentesis may isolate the
organism.
Chest x-ray makes the diagnosis of lung abscess showing the cavitary lesion with an air
fluid level. Lung abscesses are most commonly found in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe. Chest CT scan can localize and size the lesion and assist in differentiating lung abscesses from other pathologic processes (e.g., tumor, empyema, infected bulla,).
The treatment of lung abscess are oxygen therapy, respiratory therapy maneuver and postural drainage. Antibiotic treatment is also considered.
Bronchoscopy to assist with drainage and/or diagnosis is indicated in patients who fail to
respond to antibiotics or if there is suspected underlying malignancy.
Surgery is indicated on rare occasions (,10%) in patients with complications of
lung abscess.Complication of lung abscess are empyema, brain abscess, bronchiectasis, bronchopleural fistula and hepatobronchial fistula.