Pathology definition - Respiratory Alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis is divided into acute respiratory alkalosis and chronic respiratory alkalosis. Acute respiratory alkalosis is caused by cirrhosis, overdose of salicylate, hyperventilation and bacterial septicemia. Pregnancy and high altitude is associated with chronic respiratory alkalosis.
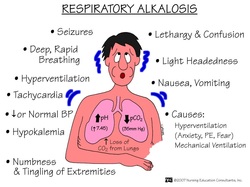
Patient with respiratory alkalosis may present with symptoms and signs such as light headedness, paraesthesia, tingling in the distal extremities, numbness around the mouth and anxiety attack as well as cardiac arrhythmias. There will be a decreased in the blood flow to the cerebrum.
In respiratory alkalosis, there will be a decreased in the partial pressure of the carbon dioxide with a compensation reaction which leads to increase renal bicarbonate secretion which cause a decrease in the level of bicarbonate.
Laboratory investigations may reveal a decreased in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide, increased in pH and decreased in bicarbonate ions.
Respiratory alkalosis is divided into acute respiratory alkalosis and chronic respiratory alkalosis. Acute respiratory alkalosis is caused by cirrhosis, overdose of salicylate, hyperventilation and bacterial septicemia. Pregnancy and high altitude is associated with chronic respiratory alkalosis.
Patient with respiratory alkalosis may present with symptoms and signs such as light headedness, paraesthesia, tingling in the distal extremities, numbness around the mouth and anxiety attack as well as cardiac arrhythmias. There will be a decreased in the blood flow to the cerebrum.
In respiratory alkalosis, there will be a decreased in the partial pressure of the carbon dioxide with a compensation reaction which leads to increase renal bicarbonate secretion which cause a decrease in the level of bicarbonate.
Laboratory investigations may reveal a decreased in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide, increased in pH and decreased in bicarbonate ions.
