|
|
|
Medicine Notes- Clinical Procedures- Punch Skin biopsy
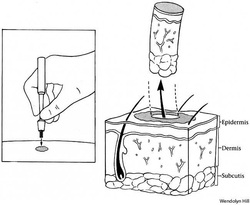
Punch skin biopsy
Punch skin biopsy is performed to identify the causes of rashes or lesions which are suspicious in nature. However, punch biopsy is not considered in case of melanoma is suspected. In melanoma, excisional biopsy is considered than punch skin biopsy. Excisional biopsy is also considered in cases of deep structure involvement.
The first step is to get the consent from patient after taking the whole history and perform a clinical examination and evaluation of the patient’s well being and the lesions.
Before starting the procedure, make sure that the patient does not present with any condition that may contraindicate punch skin biopsy.
e.g Punch skin biopsy is avoided in patient with bleeding and clotting abnormalities. Patient with INR less than 3 and platelet count less than 5 x 10*9 per liter.
Make sure that you get all the equipment require such as sterile gloves, skin marker, sterile drapes,alcohol, punch biopsy implement, gauze, local anesthetic,syringe, scissors, toothed forceps, histology pot and vaseline
The procedure begins, with choosing the area to be biopsied. The area should contain the fresh lesion which could provide a diagnostic and clear histological feature of the lesions.
Skin marker is used to mark the area as the lesion ( red scaly lesion) may loss after rubbing the skin that is being blenched with adrenaline. Skin marker is a marker for the lesion.
Alcohol swab is used to wipe the area of the lesion.
This is follow later with the introduction of the local anesthetics which is 1% lidocaine with adrenaline ( 1: 200 000) which is causing slight pain /sting in nature. These adrenaline containing anesthetic should not be used in areas which may occlude the end artery such as the penis, fingers or toe. This local anesthetic with adrenaline is injected beneath and around the site of biopsy with the aim to raise a bleb. the local anesthetic and adrenaline should enter the dermis and subcurtis. It is important to raise the bleb as it provides more spaces/depth between the surface and deep structure thus protecting the facial nerve or tendons on the dorsum of the hand.
Hand need to be washed and later the area around the biopsy sites need to be cleansed.
Sterile drapes is applied.
The sites of the skin with the marker then is placed with the punch biopsy. The punch biopsy is pushed in a rotating motion to penetrate the dermis and subcurtis which is later feel as resistance to the rotating movement. Punch biopsy usually involves area with sizes from 3- 8 mm. The punch biopsy implement is put down.
The specimen is picked up with a toothed forceps.
The specimen is harvested by cutting the connecting subcutaneous tissue. Then the specimen is placed in a histology pot.
Vaseline is applied to the wound. If the sizes of the biopsy is 8 mm a buried subcuticular suture and surface suture are required which follow later with dressing or plaster.
The common complication of performing punch skin biopsy are:
Hemorrhage
infection
Scars ( keloid scar if biopsy is taken from a keloid prone area such as the neck or hypertrophic scar)
References
1.Zuber, Thomas J. “Punch Biopsy of the Skin.” American Family Physician 65, no. 6 (March 15, 2002): 1155–1158, 1161–1162, 1164.
2.De Vries, H.j.c., J.e. Zeegelaar, E. Middelkoop, G. Gijsbers, J. Van Marle, C.h.r. Wildevuur, and W. Westerhof. “Reduced Wound Contraction and Scar Formation in Punch Biopsy Wounds. Native Collagen Dermal Substitutes. A Clinical Study.” British Journal of Dermatology 132, no. 5 (1995): 690–697. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1995.tb00712.x.
3.Russell, E.Brian, Patrick R. Carrington, and Bruce R. Smoller. “Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comparison of Shave Biopsy Versus Punch Biopsy Techniques in Subtype Diagnosis.” Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 41, no. 1 (July 1999): 69–71. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(99)70409-3.
Punch skin biopsy is performed to identify the causes of rashes or lesions which are suspicious in nature. However, punch biopsy is not considered in case of melanoma is suspected. In melanoma, excisional biopsy is considered than punch skin biopsy. Excisional biopsy is also considered in cases of deep structure involvement.
The first step is to get the consent from patient after taking the whole history and perform a clinical examination and evaluation of the patient’s well being and the lesions.
Before starting the procedure, make sure that the patient does not present with any condition that may contraindicate punch skin biopsy.
e.g Punch skin biopsy is avoided in patient with bleeding and clotting abnormalities. Patient with INR less than 3 and platelet count less than 5 x 10*9 per liter.
Make sure that you get all the equipment require such as sterile gloves, skin marker, sterile drapes,alcohol, punch biopsy implement, gauze, local anesthetic,syringe, scissors, toothed forceps, histology pot and vaseline
The procedure begins, with choosing the area to be biopsied. The area should contain the fresh lesion which could provide a diagnostic and clear histological feature of the lesions.
Skin marker is used to mark the area as the lesion ( red scaly lesion) may loss after rubbing the skin that is being blenched with adrenaline. Skin marker is a marker for the lesion.
Alcohol swab is used to wipe the area of the lesion.
This is follow later with the introduction of the local anesthetics which is 1% lidocaine with adrenaline ( 1: 200 000) which is causing slight pain /sting in nature. These adrenaline containing anesthetic should not be used in areas which may occlude the end artery such as the penis, fingers or toe. This local anesthetic with adrenaline is injected beneath and around the site of biopsy with the aim to raise a bleb. the local anesthetic and adrenaline should enter the dermis and subcurtis. It is important to raise the bleb as it provides more spaces/depth between the surface and deep structure thus protecting the facial nerve or tendons on the dorsum of the hand.
Hand need to be washed and later the area around the biopsy sites need to be cleansed.
Sterile drapes is applied.
The sites of the skin with the marker then is placed with the punch biopsy. The punch biopsy is pushed in a rotating motion to penetrate the dermis and subcurtis which is later feel as resistance to the rotating movement. Punch biopsy usually involves area with sizes from 3- 8 mm. The punch biopsy implement is put down.
The specimen is picked up with a toothed forceps.
The specimen is harvested by cutting the connecting subcutaneous tissue. Then the specimen is placed in a histology pot.
Vaseline is applied to the wound. If the sizes of the biopsy is 8 mm a buried subcuticular suture and surface suture are required which follow later with dressing or plaster.
The common complication of performing punch skin biopsy are:
Hemorrhage
infection
Scars ( keloid scar if biopsy is taken from a keloid prone area such as the neck or hypertrophic scar)
References
1.Zuber, Thomas J. “Punch Biopsy of the Skin.” American Family Physician 65, no. 6 (March 15, 2002): 1155–1158, 1161–1162, 1164.
2.De Vries, H.j.c., J.e. Zeegelaar, E. Middelkoop, G. Gijsbers, J. Van Marle, C.h.r. Wildevuur, and W. Westerhof. “Reduced Wound Contraction and Scar Formation in Punch Biopsy Wounds. Native Collagen Dermal Substitutes. A Clinical Study.” British Journal of Dermatology 132, no. 5 (1995): 690–697. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1995.tb00712.x.
3.Russell, E.Brian, Patrick R. Carrington, and Bruce R. Smoller. “Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comparison of Shave Biopsy Versus Punch Biopsy Techniques in Subtype Diagnosis.” Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 41, no. 1 (July 1999): 69–71. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(99)70409-3.
