Pediatric Definition - Epiglottitis
Epiglottitis
The causes of epiglottitis include infection form Hemophilus influenzae type B, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitis.
Epiglottitis may be indentified by the cherry red inflammation sign.
The differential diagnosis of epiglottitis are angioedema, bacterial tracheitis, foreign body and peritonsillar and retropharyhgeal abscess.
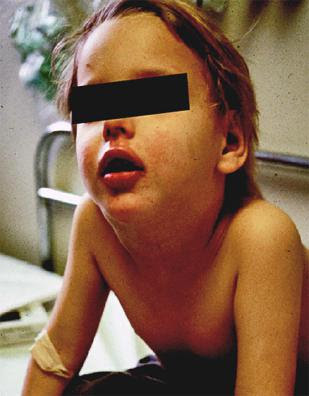
The symptoms and signs of epiglottitis are drooling, dysphagia, muffled voice, sudden onset of fever, respiratory distress, sitting in a sniffing dog position, soft stridor, cyanosis and inspiratory retractions.
Lateral neck X ray may reveal classic thumbprint sign.
The complication of epiglottitis include respiratory arrest and obstruction of the airway.
The treatment of epiglottitis may include endotracheal intubation with intravenous IV ceftriaxone and cephalosporin.
The causes of epiglottitis include infection form Hemophilus influenzae type B, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitis.
Epiglottitis may be indentified by the cherry red inflammation sign.
The differential diagnosis of epiglottitis are angioedema, bacterial tracheitis, foreign body and peritonsillar and retropharyhgeal abscess.
The symptoms and signs of epiglottitis are drooling, dysphagia, muffled voice, sudden onset of fever, respiratory distress, sitting in a sniffing dog position, soft stridor, cyanosis and inspiratory retractions.
Lateral neck X ray may reveal classic thumbprint sign.
The complication of epiglottitis include respiratory arrest and obstruction of the airway.
The treatment of epiglottitis may include endotracheal intubation with intravenous IV ceftriaxone and cephalosporin.