|
|
Pathology definition - Thrombocytopenia purpura
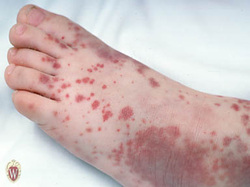
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is commonly affecting children due acute self limited reaction to viral infection. Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura is also affecting adult who suffer from chronic illness.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura may present with mucosal bleeding, purpura and petechiae.
Pathologically idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura may present with increased in the megakaryocytes in the bone marrow and enlarged platelet and thrombocytopenia will be detected in the peripheral study of the blood smears. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura occur due to splenic macrophage phagocytosis of the anti platelet IgG antibodies coat platelets. Besides that there will be an increased in the bleeding time, present of antiplatelet antibodies and decreased in the platelet count.
idiopathic thrombocytopenia is treated with prednisolone and splenectomy.
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura is commonly affecting women.The common signs and symptoms are increased in the indirect bilirubin and jaundice ( due to microangiopathic hemolytic anemia ) , decreased in the Hgb, increased in the bleeding time, renal insufficiency, azotemia, decreased in the number of platelet, fever, purpura and petechiae.
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura may be treated with plasmapheresis and splenectomy. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura may occur due to estrogens, antibiotics or viral infection. Reticulocytosis, schistocytes and thrombocytopenia are the common finding of the peripheral blood smears. Besides that the there will be microthrombi in the microvasculature and no inflammation is detected.
References
1.George, James N. “Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura.” New England Journal of Medicine 354, no. 18 (2006): 1927–1935. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp053024.
2.Burns, Terry R., and Abdus Saleem. “Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura.” The American Journal of Medicine 75, no. 6 (December 1983): 1001–1007.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is commonly affecting children due acute self limited reaction to viral infection. Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura is also affecting adult who suffer from chronic illness.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura may present with mucosal bleeding, purpura and petechiae.
Pathologically idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura may present with increased in the megakaryocytes in the bone marrow and enlarged platelet and thrombocytopenia will be detected in the peripheral study of the blood smears. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura occur due to splenic macrophage phagocytosis of the anti platelet IgG antibodies coat platelets. Besides that there will be an increased in the bleeding time, present of antiplatelet antibodies and decreased in the platelet count.
idiopathic thrombocytopenia is treated with prednisolone and splenectomy.
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura is commonly affecting women.The common signs and symptoms are increased in the indirect bilirubin and jaundice ( due to microangiopathic hemolytic anemia ) , decreased in the Hgb, increased in the bleeding time, renal insufficiency, azotemia, decreased in the number of platelet, fever, purpura and petechiae.
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura may be treated with plasmapheresis and splenectomy. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura may occur due to estrogens, antibiotics or viral infection. Reticulocytosis, schistocytes and thrombocytopenia are the common finding of the peripheral blood smears. Besides that the there will be microthrombi in the microvasculature and no inflammation is detected.
References
1.George, James N. “Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura.” New England Journal of Medicine 354, no. 18 (2006): 1927–1935. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp053024.
2.Burns, Terry R., and Abdus Saleem. “Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura.” The American Journal of Medicine 75, no. 6 (December 1983): 1001–1007.
