Pathology definition - Gout
Gout
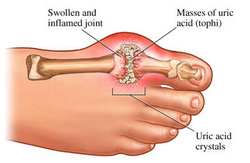
Gout may present with sudden onset of swollen tender joint mostly affecting the podagra or metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe, knee or ankles. Gout occur due to the present of urate crystal and neutrophils in the synovial fluid. The urate crystal is needle shaped, negatively birefringent crystal. The deposition of the urate crystal may lead to erosion of the cartilage.
Gout may also present with tophi which develop few months later. Tophi may present on the feet, hands or ears. Tophi occur as a result of cluster of urate crystal which is surrounded by lymphocytes, fibroblast and giant cells in the cartilage.
The common complication of gout include urate nephropathy due to deposition of the urate crystal and the formation of the uric acid stones.
Gout is treated with NSAIDS, allopurinol or probenicid.
Gout is caused mostly by hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia will later lead to formation of urate crystal which deposited in the joint. Gout is an inflammation reaction with raised ESR.
Male, middle aged, obese and increase intake of alcohol are more susceptible in developing gout.Certain condition such as deficiency of HGPRT/ Lesch- Nyhan syndrome, renal disease or neoplastic disorder may also lead to gout.
Pseudogout is often mistaken for gout. In pseudogout there will be no deposition of the urate crystal. There is normal urate level. However, there will be deposition of the calcium pyrophosphate crystal/ basophilic rhomboid crystal.
Gout may present with sudden onset of swollen tender joint mostly affecting the podagra or metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe, knee or ankles. Gout occur due to the present of urate crystal and neutrophils in the synovial fluid. The urate crystal is needle shaped, negatively birefringent crystal. The deposition of the urate crystal may lead to erosion of the cartilage.
Gout may also present with tophi which develop few months later. Tophi may present on the feet, hands or ears. Tophi occur as a result of cluster of urate crystal which is surrounded by lymphocytes, fibroblast and giant cells in the cartilage.
The common complication of gout include urate nephropathy due to deposition of the urate crystal and the formation of the uric acid stones.
Gout is treated with NSAIDS, allopurinol or probenicid.
Gout is caused mostly by hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia will later lead to formation of urate crystal which deposited in the joint. Gout is an inflammation reaction with raised ESR.
Male, middle aged, obese and increase intake of alcohol are more susceptible in developing gout.Certain condition such as deficiency of HGPRT/ Lesch- Nyhan syndrome, renal disease or neoplastic disorder may also lead to gout.
Pseudogout is often mistaken for gout. In pseudogout there will be no deposition of the urate crystal. There is normal urate level. However, there will be deposition of the calcium pyrophosphate crystal/ basophilic rhomboid crystal.
