|
|
Pathology definition - Aortic dissection
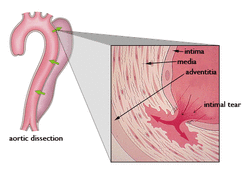
Aortic dissection
Patient who suffer from aortic dissection may present with signs and symptoms such as chest pain which is sudden and severe in nature. The chest pain may be tearing in characteristic and radiating to the back.
Aortic dissection occur due to severe hypertension or traumatic injury. Other risk factors of developing aortic dissection may includes coarctation of the aorta, Ehlers - Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome and bicuspid aortic valve.
Aortic dissection may present with teat in the tunica intima which leads to the formation of the hematoma of the intramural. There will be cystic medial necrosis.
The common complication of aortic dissection may include cardiac tamponade and aortic rupture.
The treatment of aortic dissection may include preventing from doing any tasks that may lead to rise in the blood pressure. Hypertensive patient should be treated with antihypertensive medication. Surgical repair may also be considered.
References
1.Khan, Ijaz A., and Chandra K. Nair. “CLinical, Diagnostic, and Management Perspectives of Aortic Dissection*.” CHEST Journal 122, no. 1 (July 1, 2002): 311–328. doi:10.1378/chest.122.1.311.
2.Larson, Eric W., and William D. Edwards. “Risk Factors for Aortic Dissection: A Necropsy Study of 161 Cases.” The American Journal of Cardiology 53, no. 6 (March 1, 1984): 849–855. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(84)90418-1.
Patient who suffer from aortic dissection may present with signs and symptoms such as chest pain which is sudden and severe in nature. The chest pain may be tearing in characteristic and radiating to the back.
Aortic dissection occur due to severe hypertension or traumatic injury. Other risk factors of developing aortic dissection may includes coarctation of the aorta, Ehlers - Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome and bicuspid aortic valve.
Aortic dissection may present with teat in the tunica intima which leads to the formation of the hematoma of the intramural. There will be cystic medial necrosis.
The common complication of aortic dissection may include cardiac tamponade and aortic rupture.
The treatment of aortic dissection may include preventing from doing any tasks that may lead to rise in the blood pressure. Hypertensive patient should be treated with antihypertensive medication. Surgical repair may also be considered.
References
1.Khan, Ijaz A., and Chandra K. Nair. “CLinical, Diagnostic, and Management Perspectives of Aortic Dissection*.” CHEST Journal 122, no. 1 (July 1, 2002): 311–328. doi:10.1378/chest.122.1.311.
2.Larson, Eric W., and William D. Edwards. “Risk Factors for Aortic Dissection: A Necropsy Study of 161 Cases.” The American Journal of Cardiology 53, no. 6 (March 1, 1984): 849–855. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(84)90418-1.
