Pathology definition - Sjorgen Syndrome
Sjorgen syndrome
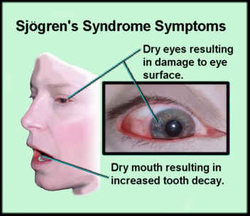
Sjorgen syndrome may present with xerostomia/ dry mouth, xerophthalmia/dry eyes and rheumatic arthritis in most case.
Sjorgen syndrome occur due to autoimmune destruction of the salivary gland and lacrimal gland. Sjorgen syndrome may present with lymphocytic infiltration of the periductal and perivascular. There will be ductal epithelial cell hyperplasia, lymphoid follicle and tissue atrophy. Sjorgen syndrome may also present with enlargement of the parotid gland and conjunctivitis. There are strong association between Sjorgen syndrome and HLA DR 2 and HLA DR 3
Laboratory investigation may reveal the present of autoantibodies such as SS-B ( La) , SS- A( Ro) and rheumatoid factor.
The complication of Sjorgen syndrome may include increase risk of developing B cell lymphoma and involvement of extraglandular tissue or exocrine glands.
The treatment may follow increase in fluid intake and consider artificial tears.
Sjorgen syndrome may present with xerostomia/ dry mouth, xerophthalmia/dry eyes and rheumatic arthritis in most case.
Sjorgen syndrome occur due to autoimmune destruction of the salivary gland and lacrimal gland. Sjorgen syndrome may present with lymphocytic infiltration of the periductal and perivascular. There will be ductal epithelial cell hyperplasia, lymphoid follicle and tissue atrophy. Sjorgen syndrome may also present with enlargement of the parotid gland and conjunctivitis. There are strong association between Sjorgen syndrome and HLA DR 2 and HLA DR 3
Laboratory investigation may reveal the present of autoantibodies such as SS-B ( La) , SS- A( Ro) and rheumatoid factor.
The complication of Sjorgen syndrome may include increase risk of developing B cell lymphoma and involvement of extraglandular tissue or exocrine glands.
The treatment may follow increase in fluid intake and consider artificial tears.
