Pathology definition - Osteopetrosis
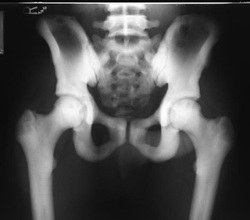
Osteopetrosis
Osteopetrosis may present with multiple symptoms and signs such as multiple fracture of the bones, cranial nerve palsies, facial paralysis, deafness, nerve compression, blindness, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, extramedullary hematopoiesis and anemia. The treatment will focus on transplant of the bone marrow and corticosteroid.
Osteopetrosis occur due to decfective in the bone resorption due to dysfunction of the activity of the osteoclast. Osteopetrosis is an autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant disorders.
Osteopetrosis is usually presented with lacking of hematopoietic marrow and lack of trabeculae. There will be a calcified cartilage known as primary spongiosa that present during the endochondral bone development. Erlenmeyer flask may present. Erlenmeyer flask is widening of the ends of the bone.
Osteopetrosis may present with multiple symptoms and signs such as multiple fracture of the bones, cranial nerve palsies, facial paralysis, deafness, nerve compression, blindness, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, extramedullary hematopoiesis and anemia. The treatment will focus on transplant of the bone marrow and corticosteroid.
Osteopetrosis occur due to decfective in the bone resorption due to dysfunction of the activity of the osteoclast. Osteopetrosis is an autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant disorders.
Osteopetrosis is usually presented with lacking of hematopoietic marrow and lack of trabeculae. There will be a calcified cartilage known as primary spongiosa that present during the endochondral bone development. Erlenmeyer flask may present. Erlenmeyer flask is widening of the ends of the bone.
