Pathology definition - Patau Syndrome
Patau Syndrome
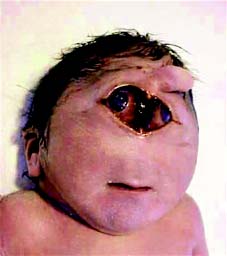
Patau syndrome may present with symptoms and signs such as holoprosencephaly, cleft lip, cleft palate, rocker bottom feet, polydactyly, microcephaly, congenital renal defect, congenital heart defect, microphthalmia or small eyes and umbilical hernia. Patau syndrome may lead to fatality within one year of birth.
Patau syndrome is associated with trisomy 13. Trisomy 13 is associated with meiotic non disjunction. Patau syndrome may also occur due to translocation between chromosome 13 and chromosome 14 and also occur due to mitotic non disjunction of chromosome 13. In this case, Patau syndrome is associated with mosaicism and the incidence increase with increasing maternal age.
Patau syndrome may present with symptoms and signs such as holoprosencephaly, cleft lip, cleft palate, rocker bottom feet, polydactyly, microcephaly, congenital renal defect, congenital heart defect, microphthalmia or small eyes and umbilical hernia. Patau syndrome may lead to fatality within one year of birth.
Patau syndrome is associated with trisomy 13. Trisomy 13 is associated with meiotic non disjunction. Patau syndrome may also occur due to translocation between chromosome 13 and chromosome 14 and also occur due to mitotic non disjunction of chromosome 13. In this case, Patau syndrome is associated with mosaicism and the incidence increase with increasing maternal age.
