Pediatric Definition - Fanconi Anemia
Fanconi Anemia
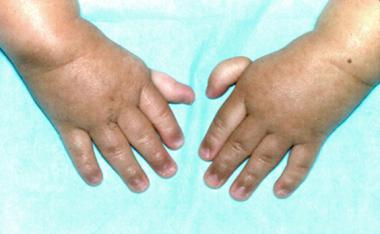
Fanconi anemia may present with symptoms and signs such as thrombocytopenia ( petechiae, purpura and bleeding), anemia ( pallor, fatigue, weak), neutropenia ( recurrent infection ), skeletal abnormalities such as hypoplasia or absence of radius or thumbs,cafe au lait spots, hyperpigmentation, horseshoe kidney, renal aplasia and collecting system duplication, short stature, microphthalmia, stabimus, hypogenitalism, ear anomalies and microcephaly.
Fanconi anemia is a genetic disorder due to autosomal recessive mutation which affect / leads to defective DNA repair.
The investigation may reveal elevation of the fetal hemoglobin level and macrocytosis.
The treatment of fanconi anemia may include bone marrow transplantation, oxymetholone or blood transfusion ( be careful that thrombocytopenia refractory to platelet transfusion ). Treat the underlying symptoms such as fever and infection with antibiotics.
Fanconi anemia may present with symptoms and signs such as thrombocytopenia ( petechiae, purpura and bleeding), anemia ( pallor, fatigue, weak), neutropenia ( recurrent infection ), skeletal abnormalities such as hypoplasia or absence of radius or thumbs,cafe au lait spots, hyperpigmentation, horseshoe kidney, renal aplasia and collecting system duplication, short stature, microphthalmia, stabimus, hypogenitalism, ear anomalies and microcephaly.
Fanconi anemia is a genetic disorder due to autosomal recessive mutation which affect / leads to defective DNA repair.
The investigation may reveal elevation of the fetal hemoglobin level and macrocytosis.
The treatment of fanconi anemia may include bone marrow transplantation, oxymetholone or blood transfusion ( be careful that thrombocytopenia refractory to platelet transfusion ). Treat the underlying symptoms such as fever and infection with antibiotics.