Pathology definition - Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency may lead to rickets and osteomalacia. Rickets mostly occur in childhood while osteomalacia typically affect the adult. Vitamin D deficiency may lead to decrease in the calcification of the osteoid matrix due to decrease in the absorption of calcium
Malnutrition, liver disease, malabsorption due to inflammatory bowel disease or pancreatic insufficiency, inadequate exposure to sunlight and defect in the synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D due to renal disease are the main causes of vitamin D deficiency. Renal osteodystrophy is the term used to describe osteomalacia that occur due to renal disease which impair the synthesis of vitamin D. There will be an unmineralized matrix of the bone which are surrounded by unmineralized osteoid. Only the trabeculae have core of calcified bone.
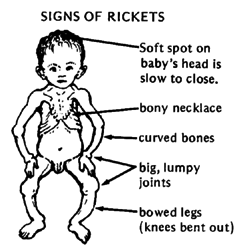
Rickets may present with protrusion of the sternum / pigeon chest, thinning of the parietal bone and occipital bone/ craniotabes, short stature, thickening of the costochondral junction/rachitic rosary and deformities of the skeleton due to defect in mineralization at the epiphyseal plate.
Patient with osteomalacia may complain of weakness of the muscle and diffuse pain in the bone. There will be radiolucency with cortical bone thinning on radiography.
The treatment of vitamin D deficiency may include treatment of underlying disorder and consider supplementation of Vitamin D.
Vitamin D deficiency may lead to rickets and osteomalacia. Rickets mostly occur in childhood while osteomalacia typically affect the adult. Vitamin D deficiency may lead to decrease in the calcification of the osteoid matrix due to decrease in the absorption of calcium
Malnutrition, liver disease, malabsorption due to inflammatory bowel disease or pancreatic insufficiency, inadequate exposure to sunlight and defect in the synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D due to renal disease are the main causes of vitamin D deficiency. Renal osteodystrophy is the term used to describe osteomalacia that occur due to renal disease which impair the synthesis of vitamin D. There will be an unmineralized matrix of the bone which are surrounded by unmineralized osteoid. Only the trabeculae have core of calcified bone.
Rickets may present with protrusion of the sternum / pigeon chest, thinning of the parietal bone and occipital bone/ craniotabes, short stature, thickening of the costochondral junction/rachitic rosary and deformities of the skeleton due to defect in mineralization at the epiphyseal plate.
Patient with osteomalacia may complain of weakness of the muscle and diffuse pain in the bone. There will be radiolucency with cortical bone thinning on radiography.
The treatment of vitamin D deficiency may include treatment of underlying disorder and consider supplementation of Vitamin D.
