Pediatric Definition - Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is life threatening condition which occurs after exposure to allergen that person sensitive with.
The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis are respiratory failure, anxiety attack and hereditary angioedema.
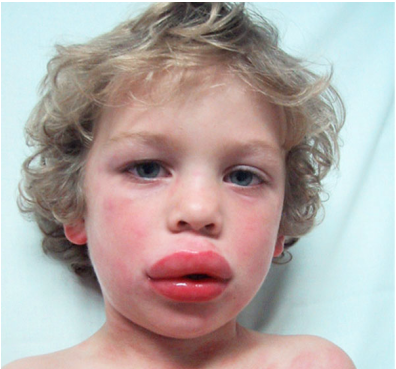
Patient may develop symptoms and signs of anaphylaxis such as shock, wheezing, pruritus, urticaria, angioedema, swollen tongue, swollen lips, swollen uvula, dyspnea, vomiting, hypotension and crampy abdominal pain.
There will be elevation of the hematocrit, elevation of the tryptase and elevation of the serum AST, LDH and creatine kinase.
Patient may develop hypercapnia, hypoxemia and acidosis detected by arterial blood gas.
The treatments of anaphylaxis are stabilizing the airway, breathing and circulation,epinephrine, ranitidine, fluid for treating hypotension, bronchodilator for cases of bronchospasm and corticosteroid as well as vasopressin.
Anaphylaxis is life threatening condition which occurs after exposure to allergen that person sensitive with.
The differential diagnosis of anaphylaxis are respiratory failure, anxiety attack and hereditary angioedema.
Patient may develop symptoms and signs of anaphylaxis such as shock, wheezing, pruritus, urticaria, angioedema, swollen tongue, swollen lips, swollen uvula, dyspnea, vomiting, hypotension and crampy abdominal pain.
There will be elevation of the hematocrit, elevation of the tryptase and elevation of the serum AST, LDH and creatine kinase.
Patient may develop hypercapnia, hypoxemia and acidosis detected by arterial blood gas.
The treatments of anaphylaxis are stabilizing the airway, breathing and circulation,epinephrine, ranitidine, fluid for treating hypotension, bronchodilator for cases of bronchospasm and corticosteroid as well as vasopressin.