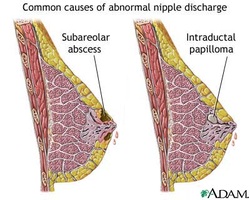
Duct ectasia typically affecting fifth decade patient and present with thick creamy discharge and retroareolar pain. Witch’s milk is a discharge from the newborn’s nipple. It affect both sexes because of the passage of female hormones across the placenta. Nipple discharge is prominent during lactation as well as pregnancy. Fibroadenosis is characterized by cycle of mastalgia with greenish colored discharged. Serous or milky discharge may occur during puberty. Milky discharge which is profuse in nature and amenorrhea is highly suggestive of prolactinoma /tumor of the anterior pituitary gland. Blood staines discharge may be dark brown in color or frank red blood. It is important to assess either there is any underlying lump or blood come from one or more duct.
Look for any evidence suggestive of duct ectasia such as nipple retraction, lumpiness and retroareolar tenderness. Paget’s disease is detected by identifying any destructive nipple. Look for any obvious stained on the clothes and identify the color. Palpate for any lump which may occur due to malignancy. Observe for any signs of abscess and infection. Visual field is assessed in case of prolactinoma. This is based on the fact that the optic chiasm is impinged by the macroadenoma from the anterior pituitary gland. Prolactinoma is associated with infertility, amenorrhea and galactorrhea. Blood can be express manually by applying pressure on the specific area of the breast. ( in case of breast carcinoma). Further investigations is required in cases of male nipple discharge.
The laboratory investigations require are full blood count, ESR, dipstick testing, FNAC and swabs, CT scan of the head, microdochectomy and mammography.
In term of full blood count, there will be a raise in white cell count due to infection. Tuberculosis and tumor may present with raise ESR. Dipstick testing is useful to differentiate between fluid and bloody discharge. FNAC is useful for detection of breast carcinoma while swab of the discharge is considered for culture and sensitivity to detect any signs of tuberculosis, abscess and infection. CT scan is useful to detect prolactinoma of the pituitary gland. Microdochectomy is useful to differentiate between intraduct papilloma and intraduct carcinoma. It is a surgical investigation and is considered if bleeding localized to individual ducts. Duct etasia and mammography is detected through mammography
Look for any evidence suggestive of duct ectasia such as nipple retraction, lumpiness and retroareolar tenderness. Paget’s disease is detected by identifying any destructive nipple. Look for any obvious stained on the clothes and identify the color. Palpate for any lump which may occur due to malignancy. Observe for any signs of abscess and infection. Visual field is assessed in case of prolactinoma. This is based on the fact that the optic chiasm is impinged by the macroadenoma from the anterior pituitary gland. Prolactinoma is associated with infertility, amenorrhea and galactorrhea. Blood can be express manually by applying pressure on the specific area of the breast. ( in case of breast carcinoma). Further investigations is required in cases of male nipple discharge.
The laboratory investigations require are full blood count, ESR, dipstick testing, FNAC and swabs, CT scan of the head, microdochectomy and mammography.
In term of full blood count, there will be a raise in white cell count due to infection. Tuberculosis and tumor may present with raise ESR. Dipstick testing is useful to differentiate between fluid and bloody discharge. FNAC is useful for detection of breast carcinoma while swab of the discharge is considered for culture and sensitivity to detect any signs of tuberculosis, abscess and infection. CT scan is useful to detect prolactinoma of the pituitary gland. Microdochectomy is useful to differentiate between intraduct papilloma and intraduct carcinoma. It is a surgical investigation and is considered if bleeding localized to individual ducts. Duct etasia and mammography is detected through mammography