Pathology definition - Fragile X Snydrome
Fragile X syndrome
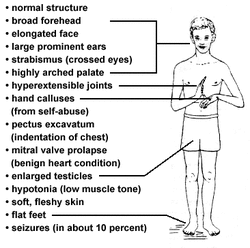
Fragile X syndrome may present with certain characteristic such as mitral valve prolapse, autism, mental retardation, elongated face with large ear and large jaw. Patient may also present with hyperextensible joints and macro orchidism or large testicles. Fragile X Syndrome affect male mostly with more prominent clinical feature.
Fragile X syndrome may present due to increase in the number CGG repeats in the FMR-1 gene on the X chromosome. FMR-1 gene is a familial metal retardation gene.
Fragile X syndrome may show sign of anticipation where the number of repeats increases with time from one generation to another which result in more severe outcomes. Other disorders with anticipation include Huntington disease and myotonic dystrophy.
Fragile X syndrome may present with certain characteristic such as mitral valve prolapse, autism, mental retardation, elongated face with large ear and large jaw. Patient may also present with hyperextensible joints and macro orchidism or large testicles. Fragile X Syndrome affect male mostly with more prominent clinical feature.
Fragile X syndrome may present due to increase in the number CGG repeats in the FMR-1 gene on the X chromosome. FMR-1 gene is a familial metal retardation gene.
Fragile X syndrome may show sign of anticipation where the number of repeats increases with time from one generation to another which result in more severe outcomes. Other disorders with anticipation include Huntington disease and myotonic dystrophy.
